EIF2AK2 protein targeted activation of AIM2-mediated PANoptosis promotes sepsis-induced acute kidney injury
- PMID: 39311631
- PMCID: PMC11421145
- DOI: 10.1080/0886022X.2024.2403649
EIF2AK2 protein targeted activation of AIM2-mediated PANoptosis promotes sepsis-induced acute kidney injury
Abstract
Background: Acute kidney injury (AKI) frequently occurs as a complication of sepsis. PANoptosis refers to a type of inflammatory programmed cell death that exhibits key characteristics of apoptosis, necroptosis, and pyroptosis. Here, we evaluated the role of absent in melanoma 2 (AIM2) and eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 alpha kinase 2 (EIF2AK2) in septic AKI.
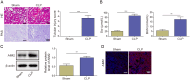
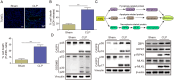
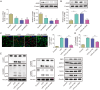
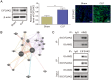
Methods: A septic AKI model was created through cecal ligation and puncture (CLP), while an in vitro model was developed using lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated HK2 cells. Hematoxylin and eosin (HE), Periodic acid-Schiff (PAS), and TUNEL staining were conducted to assess kidney injury in mice. Levels of serum creatinine (Scr) and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) were detected by kits. Gene expression was detected utilizing RT-qPCR, and Western blot was used to test protein levels. Immunofluorescence was employed to measure EIF2AK2 and AIM2 expression in mouse kidney tissue. Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) activity assay was conducted to evaluate cytotoxicity. Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) was performed to verify the binding relationship between EIF2AK2 and AIM2.
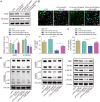
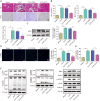
Results: AIM2 expression was increased in the renal tissue of mice subjected to CLP. Activation of the inflammasome and PANoptosis were observed in the renal tissue of CLP mice. AIM2 depletion attenuated PANoptosis in LPS-treated HK-2 cells. Additionally, EIF2AK2 could directly target AIM2, leading to a positive regulation of AIM2 expression. Notably, EIF2AK2 induced PANoptosis through upregulating AIM2 in HK-2 cells stimulated by LPS.
Conclusions: Our results revealed the important role of EIF2AK2-induced AIM2 upregulation in the activation of PANoptosis during septic AKI.
Keywords: AIM2; Acute kidney injury; EIF2AK2; PANoptosis; sepsis.
Plain language summary
Renal tissue from CLP mice exhibited an increase in AIM2 expression.Renal tissue from CLP mice demonstrated inflammasome activation and PANoptosis.AIM2 silencing reduced PANoptosis in LPS-treated HK-2 cells.EIF2AK2 directly targeted AIM2 and positively regulated its expression.EIF2AK2 promoted PANoptosis via AIM2 in LPS-triggered HK-2 cells.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cytosolic mtDNA-cGAS-STING axis contributes to sepsis-induced acute kidney injury via activating the NLRP3 inflammasome.Clin Exp Nephrol. 2024 May;28(5):375-390. doi: 10.1007/s10157-023-02448-5. Epub 2024 Jan 19. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 38238499
-
β-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Alleviates Sepsis-associated Acute Kidney Injury by Activating NAD+/SIRT3 Signaling.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2025 Jun;83(2):2089-2099. doi: 10.1007/s12013-024-01619-9. Epub 2024 Nov 23. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2025. PMID: 39580586
-
The interaction between C/EBPβ and TFAM promotes acute kidney injury via regulating NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis.Mol Immunol. 2020 Nov;127:136-145. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2020.08.023. Epub 2020 Sep 21. Mol Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32971400
-
AIM2 mediated neuron PANoptosis plays an important role in diabetes cognitive dysfunction.Behav Brain Res. 2025 Aug 5;491:115651. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2025.115651. Epub 2025 May 20. Behav Brain Res. 2025. PMID: 40404017 Review.
-
Emerging role of PANoptosis in kidney diseases: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities.Apoptosis. 2025 Apr;30(3-4):579-596. doi: 10.1007/s10495-024-02072-y. Epub 2025 Jan 20. Apoptosis. 2025. PMID: 39833634 Review.
Cited by
-
Biological characteristics, immune infiltration and drug prediction of PANoptosis related genes and possible regulatory mechanisms in inflammatory bowel disease.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 15;15(1):2033. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-84911-1. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39814753 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling PANoptosis in Acute Kidney Injury: An Integrative Multi-Dimensional Approach to Identify Key Biomarkers.J Inflamm Res. 2025 Jul 2;18:8735-8754. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S525222. eCollection 2025. J Inflamm Res. 2025. PMID: 40620603 Free PMC article.
-
PANoptosis in Sepsis: A Central Role and Emerging Therapeutic Target.J Inflamm Res. 2025 May 13;18:6245-6261. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S513367. eCollection 2025. J Inflamm Res. 2025. PMID: 40386177 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
