Zona Incerta GABAergic Neurons Facilitate Emergence from Isoflurane Anesthesia in Mice
- PMID: 39312079
- PMCID: PMC11502554
- DOI: 10.1007/s11064-024-04230-9
Zona Incerta GABAergic Neurons Facilitate Emergence from Isoflurane Anesthesia in Mice
Abstract
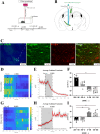
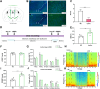
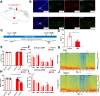
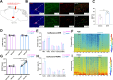
The zona incerta (ZI) predominantly consists of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABAergic) neurons, located adjacent to the lateral hypothalamus. GABA, acting on GABAA receptors, serves as a crucial neuromodulator in the initiation and maintenance of general anesthesia. In this study, we aimed to investigate the involvement of ZI GABAergic neurons in the general anesthesia process. Utilizing in-vivo calcium signal optical fiber recording, we observed a decrease in the activity of ZI GABAergic neurons during isoflurane anesthesia, followed by a significant increase during the recovery phase. Subsequently, we selectively ablated ZI GABAergic neurons to explore their role in general anesthesia, revealing no impact on the induction of isoflurane anesthesia but a prolonged recovery time, accompanied by a reduction in delta-band power in mice under isoflurane anesthesia. Finally, through optogenetic activation/inhibition of ZI GABAergic neurons during isoflurane anesthesia, we discovered that activation of these neurons facilitated emergence without affecting the induction process, while inhibition delayed emergence, leading to fluctuations in delta band activity. In summary, these findings highlight the involvement of ZI GABAergic neurons in modulating the emergence of isoflurane anesthesia.
Keywords: Emergence time; GABAergic Neurons; Isoflurane Anesthesia; Optogenetic; Zona Incerta.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
GABAergic Neurons in the Central Amygdala Promote Emergence from Isoflurane Anesthesia in Mice.Anesthesiology. 2025 Feb 1;142(2):278-297. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000005279. Epub 2024 Oct 28. Anesthesiology. 2025. PMID: 39466630 Free PMC article.
-
Reactive astrocytes mediate postoperative surgery-induced anxiety through modulation of GABAergic signalling in the zona incerta of mice.Br J Anaesth. 2025 Jan;134(1):111-123. doi: 10.1016/j.bja.2024.08.043. Epub 2024 Nov 26. Br J Anaesth. 2025. PMID: 39592364
-
[Activation of GABAergic neurons in the zona incerta accelerates anesthesia induction with sevoflurane and propofol without affecting anesthesia maintenance or awakening in mice].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2023 May 20;43(5):718-726. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2023.05.06. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2023. PMID: 37313812 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Ventral Tegmental Area Glutamatergic Neurons Facilitated Emergence From Isoflurane Anesthesia Involves Excitation of Lateral Septum GABA-ergic Neurons in Mice.Anesth Analg. 2024 Aug 1;139(2):397-410. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000006739. Epub 2023 Nov 27. Anesth Analg. 2024. PMID: 38048607
-
The zona incerta system: Involvement in Parkinson's disease.Exp Neurol. 2024 Dec;382:114992. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2024.114992. Epub 2024 Oct 10. Exp Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39393673 Review.
References
-
- Franks NP, Wisden W (2021) The inescapable drive to sleep: overlapping mechanisms of sleep and sedation. Science 374(6567):556–559 - PubMed
-
- Wang D et al (2021) GABAergic neurons in the dorsal-intermediate lateral septum regulate sleep-wakefulness and anesthesia in mice. Anesthesiology 135(3):463–481 - PubMed
-
- Franks NP (2008) General anaesthesia: from molecular targets to neuronal pathways of sleep and arousal. Nat Rev Neurosci 9(5):370–386 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

