The Innate Immune System and the TRAIL-Bcl-XL Axis Mediate a Sex Bias in Lung Cancer and Confer a Therapeutic Vulnerability in Females
- PMID: 39312191
- PMCID: PMC11649478
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-24-0585
The Innate Immune System and the TRAIL-Bcl-XL Axis Mediate a Sex Bias in Lung Cancer and Confer a Therapeutic Vulnerability in Females
Abstract
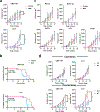
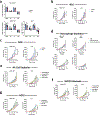
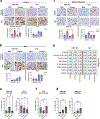
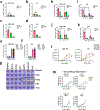
There is a significant sex bias in lung cancer, with males showing increased mortality compared with females. A better mechanistic understanding of these differences could help identify therapeutic targets to personalize cancer therapies to each sex. After observing a clear sex bias in humanized mice, with male patient-derived xenograft lung tumors being more progressive and deadlier than female patient-derived xenograft lung tumors, we identified mouse tumor models of lung cancer with the same sex bias. This sex bias was not observed in models of breast, colon, melanoma, and renal cancers. In vivo, the sex bias in growth and lethality required intact ovaries, functional innate NK cells and monocytes/macrophages, and the activating receptor NKG2D. Ex vivo cell culture models were sensitized to the anticancer effects of NKG2D-mediated NK cell and macrophage killing through the TRAIL-Bcl-XL axis when cultured with serum from female mice with intact ovaries. In both flank and orthotopic models, the Bcl-XL inhibitor navitoclax (ABT-263) improved tumor growth control in female mice and required NK cells, macrophages, and the TRAIL signaling pathway. This research suggests that navitoclax and TRAIL pathway agonists could be used as a personalized therapy to improve outcomes in women with lung cancer. Significance: Lung cancers in females are more susceptible to killing through a TRAIL-Bcl-XL axis, indicating that targeting this axis therapeutically could represent a personalized approach to treat female patients with lung cancer.
©2024 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: All authors declare they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A. Cancer Statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J Clin 2021;71:7–33 - PubMed
-
- Clocchiatti A, Cora E, Zhang Y, Dotto GP. Sexual dimorphism in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2016;16:330–9 - PubMed
-
- Tolwin Y, Gillis R, Peled N. Gender and lung cancer-SEER-based analysis. Ann Epidemiol 2020;46:14–9 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R56 AI139658/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA229812/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- RSG-21-100-01-IBCD/American Cancer Society (ACS)
- V2018-022/V Foundation for Cancer Research (VFCR)
- 5R01CA2239706-04S1/National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- R01HL162991/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
- Scholarship/King Saud University (KSU)
- R56AI139658/National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID)
- R37 CA269249/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL162991/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- CCR18548205/Susan G. Komen (SGK)
- R01 CA239706/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01CA2239706/National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- P30 CA016059/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37CA269249/National Cancer Institute (NCI)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

