Egfl6 promotes ovarian cancer progression by enhancing the immunosuppressive functions of tumor-associated myeloid cells
- PMID: 39312740
- PMCID: PMC11527450
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI175147
Egfl6 promotes ovarian cancer progression by enhancing the immunosuppressive functions of tumor-associated myeloid cells
Abstract
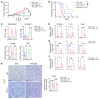
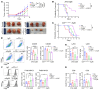
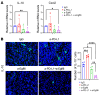
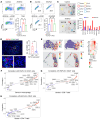
Tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) and myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) play a critical role in resistance to immunotherapy. In this study, we identified epidermal growth factor-like 6 (Egfl6) as a regulator of myeloid cell functions. Our analyses indicated that Egfl6, via binding with β3 integrins and activation of p38 and SYK signaling, acts as a chemotactic factor for myeloid cell migration and promotes their differentiation toward an immunosuppressive state. In syngeneic mouse models of ovarian cancer (OvCa), tumor expression of Egfl6 increased the intratumoral accumulation of polymorphonuclear (PMN) MDSCs and TAMs and their expression of immunosuppressive factors, including CXCL2, IL-10, and PD-L1. Consistent with this, in an immune 'hot' tumor model, Egfl6 expression eliminated response to anti-PD-L1 therapy, while Egfl6 neutralizing antibody decreased the accumulation of tumor-infiltrating CD206+ TAMs and PMN-MDSCs and restored the efficacy of anti-PD-L1 therapy. Supporting a role in human tumors, in human OvCa tissue samples, areas of high EGFL6 expression colocalized with myeloid cell infiltration. scRNA-Seq analyses revealed a correlation between EGFL6 and immune cell expression of immunosuppressive factors. Our data provide mechanistic insights into the oncoimmunologic functions of EGFL6 in mediating tumor immune suppression and identified EGFL6 as a potential therapeutic target to enhance immunotherapy in patients with OvCa.
Keywords: Cancer immunotherapy; Immunology; Macrophages; Obstetrics/gynecology; Oncology.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Expression and prognostic value of EGF-like domain multiple 6 in uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma and its correlation with immune cell infiltration.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 2;15(1):22620. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-07379-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40595086 Free PMC article.
-
USP14-IMP2-CXCL2 axis in tumor-associated macrophages facilitates resistance to anti-PD-1 therapy in gastric cancer by recruiting myeloid-derived suppressor cells.Oncogene. 2025 Jul;44(28):2413-2426. doi: 10.1038/s41388-025-03425-w. Epub 2025 Apr 23. Oncogene. 2025. PMID: 40269263
-
PMN-MDSCs are responsible for immune suppression in anti-PD-1 treated TAP1 defective melanoma.Clin Transl Oncol. 2025 Jul;27(7):3073-3083. doi: 10.1007/s12094-024-03840-7. Epub 2025 Jan 18. Clin Transl Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39825997
-
Unraveling the role of M2 TAMs in ovarian cancer dynamics: a systematic review.J Transl Med. 2025 Jun 3;23(1):623. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06643-8. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40462084 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Key players of immunosuppression in epithelial malignancies: Tumor-infiltrating myeloid cells and γδ T cells.Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2024 May;7(5):e2066. doi: 10.1002/cnr2.2066. Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2024. PMID: 38703051 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Expression and prognostic value of EGF-like domain multiple 6 in uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma and its correlation with immune cell infiltration.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 2;15(1):22620. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-07379-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40595086 Free PMC article.
-
Radiotherapy plus a self-gelation powder encapsulating tRF5-GlyGCC inhibitor potentiates natural kill cell immunity to prevent hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence.J Nanobiotechnology. 2025 Feb 10;23(1):100. doi: 10.1186/s12951-025-03133-3. J Nanobiotechnology. 2025. PMID: 39930495 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic reprogramming and therapeutic resistance in primary and metastatic breast cancer.Mol Cancer. 2024 Nov 21;23(1):261. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-02165-x. Mol Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39574178 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

