Mycobacterium tuberculosis VII secretion system effector molecule Rv2347c blocks the maturation of phagosomes and activates the STING/TBK1 signaling pathway to inhibit cell autophagy
- PMID: 39313213
- PMCID: PMC11537087
- DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.01188-24
Mycobacterium tuberculosis VII secretion system effector molecule Rv2347c blocks the maturation of phagosomes and activates the STING/TBK1 signaling pathway to inhibit cell autophagy
Abstract
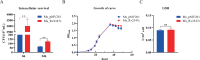
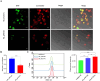
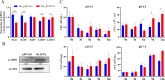
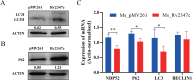
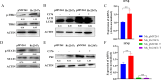
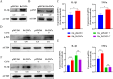
The VII secretion system is the main channel for Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) to secrete virulence proteins. The ESAT-like proteins EsxA/B and EsxW/V in the RD region of its genome have been used as targets for vaccine antigens. However, the function of EsxO/P has not been explored, although it was predicted to potentially induce Th1 cell responses as a vaccine development target. In this study, the VII secretion system effector molecule Rv2347c was heterologously expressed in Mycobacterium smegmatis and found to inhibit the expression of the early marker RAB5 of phagosomes, thus preventing the maturation process of phagosomes toward lysosomes, and activated the host cytoplasmic sensing pathway. It inhibited autophagy and activated IFNβ transcription through the STING/TBK1 pathway promoting the host's survival. Therefore, Rv2347c plays an important role in the pathogenesis of MTB with the potential to be utilized as a new target for tuberculosis vaccine development.
Importance: We found that the ESAT-like protein Rv2347c (EsxP) can inhibit the maturation of phagosomes, leading to mycobacterium escape from phagosomes into the cytoplasm, which triggers the host's cytoplasmic sensing pathway STING/TBK1, inhibiting autophagy and upregulating IFNβ transcription, which contributes to the survival of mycobacterium in the host cell. We also found that Rv2347c was able to activate host immunity by activating NF-κB via STING and promoting the transcription of downstream pro-inflammatory factors. Meanwhile, the host also produces IL-1β to repair phagosome maturation arrest via the STING-mediated non-NF-κB pathway.
Keywords: STING; autophagy; phagolysosome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The SecA2 pathway of Mycobacterium tuberculosis exports effectors that work in concert to arrest phagosome and autophagosome maturation.PLoS Pathog. 2018 Apr 30;14(4):e1007011. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007011. eCollection 2018 Apr. PLoS Pathog. 2018. PMID: 29709019 Free PMC article.
-
Mycobacterium tuberculosis EsxO (Rv2346c) promotes bacillary survival by inducing oxidative stress mediated genomic instability in macrophages.Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2016 Jan;96:44-57. doi: 10.1016/j.tube.2015.11.006. Epub 2015 Nov 24. Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2016. PMID: 26786654
-
Deciphering the functional roles of PE18 and PPE26 proteins in modulating Mycobacterium tuberculosis pathogenesis and immune response.Front Immunol. 2025 Jan 30;16:1517822. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1517822. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39949767 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of immune evasion by Mycobacterium tuberculosis: the impact of T7SS and cell wall lipids on host defenses.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2024 Oct;59(5):310-336. doi: 10.1080/10409238.2024.2411264. Epub 2024 Oct 8. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39378051 Review.
-
Infect and Inject: How Mycobacterium tuberculosis Exploits Its Major Virulence-Associated Type VII Secretion System, ESX-1.Microbiol Spectr. 2019 May;7(3):10.1128/microbiolspec.bai-0024-2019. doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.BAI-0024-2019. Microbiol Spectr. 2019. PMID: 31172908 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Deciphering tuberculosis: lysosome-centric insights into pathogenesis and therapies.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 May 14;15:1582037. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1582037. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40438237 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mycobacterium tuberculosis Sulfate Ester Dioxygenase Rv3406 Is Able to Inactivate the RCB18350 Compound.ACS Infect Dis. 2025 Apr 11;11(4):986-997. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.4c01030. Epub 2025 Mar 20. ACS Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 40111403 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Osman MM, Shanahan JK, Chu F, Takaki KK, Pinckert ML, Pagán AJ, Brosch R, Conrad WH, Ramakrishnan L. 2022. The C terminus of the mycobacterium ESX-1 secretion system substrate ESAT-6 is required for phagosomal membrane damage and virulence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 119:e2122161119. doi:10.1073/pnas.2122161119 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

