Structural insights into CXCR4 modulation and oligomerization
- PMID: 39313635
- PMCID: PMC11832422
- DOI: 10.1038/s41594-024-01397-1
Structural insights into CXCR4 modulation and oligomerization
Abstract
Activation of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 by its chemokine ligand CXCL12 regulates diverse cellular processes. Previously reported crystal structures of CXCR4 revealed the architecture of an inactive, homodimeric receptor. However, many structural aspects of CXCR4 remain poorly understood. Here, we use cryo-electron microscopy to investigate various modes of human CXCR4 regulation. CXCL12 activates CXCR4 by inserting its N terminus deep into the CXCR4 orthosteric pocket. The binding of US Food and Drug Administration-approved antagonist AMD3100 is stabilized by electrostatic interactions with acidic residues in the seven-transmembrane-helix bundle. A potent antibody blocker, REGN7663, binds across the extracellular face of CXCR4 and inserts its complementarity-determining region H3 loop into the orthosteric pocket. Trimeric and tetrameric structures of CXCR4 reveal modes of G-protein-coupled receptor oligomerization. We show that CXCR4 adopts distinct subunit conformations in trimeric and tetrameric assemblies, highlighting how oligomerization could allosterically regulate chemokine receptor function.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: All authors are employees of Regeneron Pharmaceuticals and may own stock and/or stock options of the company. W.C.O. is an officer of Regeneron. All funding for this work was provided by Regeneron Pharmaceuticals. The anti-CXCR4 antibody described in this manuscript is a subject of international patent applications (PCT/US2024/044209 and PCT/US2024/044111).
Figures

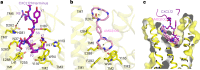












References
-
- Britton, C., Poznansky, M. C. & Reeves, P. Polyfunctionality of the CXCR4/CXCL12 axis in health and disease: implications for therapeutic interventions in cancer and immune-mediated diseases. FASEB J.35, e21260 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Guo, F. et al. CXCL12/CXCR4: a symbiotic bridge linking cancer cells and their stromal neighbors in oncogenic communication networks. Oncogene35, 816–826 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Feng, Y., Broder, C. C., Kennedy, P. E. & Berger, E. A. HIV-1 entry cofactor: functional cDNA cloning of a seven-transmembrane, G protein-coupled receptor. Science272, 872–877 (1996). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

