Study of adiponectin gene (rs1501299) polymorphism and serum adiponectin level in patients with primary knee osteoarthritis
- PMID: 39313801
- PMCID: PMC11421100
- DOI: 10.1186/s40246-024-00670-0
Study of adiponectin gene (rs1501299) polymorphism and serum adiponectin level in patients with primary knee osteoarthritis
Abstract
Background: We aimed to study, for the first time in the Egyptian population, the relationship between the serum adiponectin level in knee osteoarthritis (KOA) patients and its correlation with clinical, radiological, and ultrasonographic characteristics. Additionally, investigate the relationship between the adiponectin (ADIPOQ) gene rs1501299 (+ 276G/T) polymorphism and KOA susceptibility and severity.
Methods: This case-control study enrolled 40 patients with primary KOA and 40 matched controls. All patients underwent physical examination of the knee, pain assessment using the visual analogue scale (VAS), and functional evaluation by Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC). Severity of KOA was assessed by Kellgren Lawrence (KL) grading scale and ultrasonography grading systems. Serum adiponectin levels and adiponectin (ADIPOQ) gene single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) (rs1501299) genotyping were done for all patients and controls.
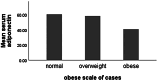
Results: The study included 40 patients with primary symptomatic KOA and 40 controls with comparable age, sex, and body mass index. The genotype of the rs1501299 (+ 276G/T) polymorphism of the ADIPOQ gene was determined using TaqMan allelic discrimination. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent test was used to measure the level of serum adiponectin. The Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis (WOMAC) score was used to assess functional capability, while the visual analogue scale was utilised to assess knee pain. Using the Kellgren-Lawrence (KL) grading method and global femoral cartilage (GFC) ultrasound grading, the severity of KOA was assessed. No significant differences between patients and controls as regards the genotype distributions and allele frequencies (p = 0.400, p = 0.507, respectively) of ADIPOQ gene rs1501299 (+ 276G/T) polymorphism. Furthermore, serum adiponectin level was significantly higher in the patients compared to healthy subjects (p < 0.001). Additionally, adiponectin level had a significant negative correlation with disease severity as evaluated by KL and GFC grading (r=-0.351, p = 0.027 and r=-0.397, p = 0.011, respectively).
Conclusions: The ADIPOQ gene rs1501299 (+ 276G/T) polymorphism was not associated with KOA severity or vulnerability. The level of adiponectin considerably reduced as the severity of KOA rose, indicating that adiponectin may have a preventive effect in KOA.
Keywords: Adiponectin; Gene polymorphism; Knee; Osteoarthritis; Ultrasonography.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Hao Z, Wang Y, Wang L, Feng Q, Li H, Chen T, Chen J, Wang J, Shi G, Chen R, Li B, Zhou S, Jin W, Li J. Burden evaluation and prediction of osteoarthritis and site-specific osteoarthritis coupled with attributable risk factors in China from 1990 to 2030. Clin Rheumatol Jun. 2024;43(6):2061–77. - PubMed
-
- Yusuf E, Nelissen RG, Ioan-Facsinay A, Stojanovic-Susulic V, DeGroot J, Van Osch G, et al. Association between weight or body mass index and hand osteoarthritis: a systematic review. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69:761–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous