Evaluation of prognostic efficacy of liver immune status index in predicting postoperative outcomes in hepatocellular carcinoma patients: A multi-institutional retrospective study
- PMID: 39313837
- PMCID: PMC11589398
- DOI: 10.1002/jhbp.12070
Evaluation of prognostic efficacy of liver immune status index in predicting postoperative outcomes in hepatocellular carcinoma patients: A multi-institutional retrospective study
Abstract
Background: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) ranks third in cancer-related deaths globally. Despite treatment advances, high post-hepatectomy recurrence rates (RR), especially with liver fibrosis and hepatitis C virus infection, remain challenging. Key prognostic factors include vascular invasion and perioperative blood loss, impacting extrahepatic recurrence. Natural killer (NK) cells are crucial in countering circulating tumor cells through TRAIL-mediated pathways. The aim of this study was to validate the liver immune status index (LISI) as a predictive tool for liver NK cell antitumor efficiency, particularly in HCC patients with vascular invasion.
Methods: A retrospective analysis of 1337 primary HCC hepatectomies was conducted by the Hiroshima Surgical Study Group of Clinical Oncology (HiSCO). Clinicodemographic data were extracted from electronic medical records. Prognostic indices (FIB-4, ALBI, ALICE, GNRI, APRI, and LISI) were evaluated using area under the receiver operating characteristic curve values. Survival analyses employed Kaplan-Meier estimations and log-rank tests.
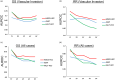
Results: LISI significantly correlated with other prognostic markers and stratified patients into risk groups with distinct overall survival (OS) and RR. It showed superior predictive performance for 2-year OS and RR, especially in patients with vascular invasion. Over longer periods, APRI and FIB-4 index reliabilities improved. The HISCO-HCC score, combining LISI, tumor burden score, and alpha-fetoprotein levels, enhanced prognostic accuracy.
Conclusion: LISI outperformed existing models, particularly in HCC with vascular invasion. The HISCO-HCC score offers improved prognostic precision, guiding immunotherapeutic strategies and individualized patient care in HCC.
Keywords: antitumor activity; hepatectomy; hepatocellular carcinoma; natural killer cells.
© 2024 The Author(s). Journal of Hepato‐Biliary‐Pancreatic Sciences published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Society of Hepato‐Biliary‐Pancreatic Surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Ko S, Kanehiro H, Hisanaga M, Nagao M, Ikeda N, Nakajima Y. Liver fibrosis increases the risk of intrahepatic recurrence after hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Br J Surg. 2002;89:57–62. - PubMed
-
- Hashimoto M, Kobayashi T, Ishiyama K, Ide K, Ohira M, Tahara H, et al. Predictive independent factors for extrahepatic metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma following curative hepatectomy. Anticancer Res. 2017;37:2625–2631. - PubMed
-
- Taketomi A, Toshima T, Kitagawa D, Motomura T, Takeishi K, Mano Y, et al. Predictors of extrahepatic recurrence after curative hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010;17:2740–2746. - PubMed
-
- Kobayashi A, Kaido T, Hamaguchi Y, Okumura S, Taura K, Hatano E, et al. Impact of postoperative changes in sarcopenic factors on outcomes after hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2016;23:57–64. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

