This is a preprint.
Non-canonical IL-22 receptor signaling remodels the mucosal barrier during fungal immunosurveillance
- PMID: 39314368
- PMCID: PMC11419061
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.09.08.611873
Non-canonical IL-22 receptor signaling remodels the mucosal barrier during fungal immunosurveillance
Abstract
Mucosal barrier integrity is vital for homeostasis with commensal organisms while preventing pathogen invasion. We unexpectedly found that fungal-induced immunosurveillance enhances resistance to fungal outgrowth and tissue invasion by remodeling the oral mucosal epithelial barrier in mouse models of adult and neonatal Candida albicans colonization. Epithelial subset expansion and tissue remodeling were dependent on interleukin-22 (IL-22) and signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) signaling, through a non-canonical receptor complex composed of glycoprotein 130 (gp130) coupled with IL-22RA1 and IL-10RB. Immunosurveillance-induced epithelial remodeling was restricted to the oral mucosa, whereas barrier architecture was reset once fungal-specific immunity developed. Collectively, these findings identify fungal-induced transient mucosal remodeling as a critical determinant of resistance to mucosal fungal infection during early stages of microbial colonization.
Keywords: Candida albicans; IL-10RB; IL-22RA1; JAK; STAT3; TYK2; Th17; Th22; gp130; oral epithelium.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
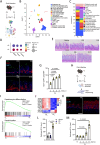
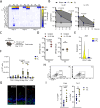

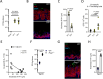
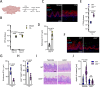
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
