Antioxidant Properties and Vasorelaxant Mechanism of Aqueous Extract of Ricinodendron heudelotii (Euphorbiaceae)
- PMID: 39314543
- PMCID: PMC11419840
- DOI: 10.1155/2024/3435974
Antioxidant Properties and Vasorelaxant Mechanism of Aqueous Extract of Ricinodendron heudelotii (Euphorbiaceae)
Abstract
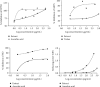
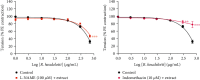
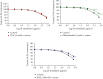
Ricinodendron heudelotii is a plant of the Euphorbiaceae family, used in traditional medicine to treat numerous diseases, including high blood pressure. The aim of this study is to evaluate the antioxidant and vasorelaxant effects of the aqueous extract of the stem bark of R. heudelotii. The pharmacological studies were carried out using the aqueous extract obtained by infusion. The antioxidant capacity of R. heudelotii was assessed by in vitro tests with DPPH (2,2-diphenyl-1-picryl-hydrazyl), ABTS (2,2'-azino-bis (3-ethylbenz-thiazoline-6-sulfonic acid), iron-reducing capacity (FRAP), and inhibition of nitric oxide (NO) release. In vitro studies, the aortic rings obtained from adult Wistar albino rats of both sexes were used to determine the vasorelaxant effects of the extract of R. heudelotii on the NO and prostacyclin (PGI2) pathways as well as its involvement on various potassium channels were determined on intact or naked fragments of rat aorta precontracted with phenylephrine (10-6 M) or KCl (60 mM). The aqueous extract of R. heudelotii exhibited a remarkable DPPH (EC50: 1.68 μg/mL) and ABTS (EC50: 106.30 μg/mL) and nitric oxide (53.71% inhibition at 1000 μg/mL) radical scavenging activities as well as reducing power (absorbance of 1.56 at 1000 μg/mL). The nitric oxide inhibitor, NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME), and prostacyclin inhibitor, indomethacin, significantly attenuated the vasodilatory effect of R. heudelotii. Tetraethylammonium could not inhibit the vasodilatory effect of the extract, unlike glibenclamide and barium chloride. Ricinodendron heudelotii extract possesses antioxidant properties and vasorelaxing effect linked to endothelium-related factors, and this relaxation was partially mediated mainly through the inhibition of Kir and KATP channels.
Keywords: endothelium; radical scavenging activities; vasodilatory effects.
Copyright © 2024 Jacquy Joyce Wanche Kojom et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Endothelium nitric oxide-independent vasorelaxant effects of the aqueous extract from Stephania abyssinica on the isolated rat thoracic aorta.J Complement Integr Med. 2015 Mar;12(1):15-21. doi: 10.1515/jcim-2014-0022. J Complement Integr Med. 2015. PMID: 25390028
-
Vasorelaxant effects of Cerebralcare Granule® are mediated by NO/cGMP pathway, potassium channel opening and calcium channel blockade in isolated rat thoracic aorta.J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 Aug 8;155(1):572-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.05.062. Epub 2014 Jun 9. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24924524
-
Vascular effects and antioxidant activity of two Combretum species from Democratic Republic of Congo.J Ethnopharmacol. 2012 Jun 26;142(1):194-200. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2012.04.039. Epub 2012 May 4. J Ethnopharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22564815
-
Vasorelaxant effect of fennel seeds (Foeniculum vulgare Mill) extracts on rat mesenteric arteries: Assessment of phytochemical profiling and antioxidant potential.Fitoterapia. 2025 Mar;181:106359. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2024.106359. Epub 2024 Dec 24. Fitoterapia. 2025. PMID: 39725088
-
Antihypertensive Effects of Aqueous Extract of Ricinodendron heudelotii (Baill.) Pierre (Euphorbiaceae) in Wistar Rat.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Nov 1;2022:3305733. doi: 10.1155/2022/3305733. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 36387352 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate)/Clay/Essential Oils Bionanocomposites Incorporating Biochar: Thermo-Mechanical and Antioxidant Properties.Polymers (Basel). 2025 Apr 24;17(9):1157. doi: 10.3390/polym17091157. Polymers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40362941 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

