Anti-CV2 Antibody-Positive Sensorimotor Polyneuropathy Following Bacillus Calmette-Guérin Intravesical Infusion Therapy
- PMID: 39314618
- PMCID: PMC11419594
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.67686
Anti-CV2 Antibody-Positive Sensorimotor Polyneuropathy Following Bacillus Calmette-Guérin Intravesical Infusion Therapy
Abstract
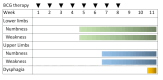
Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) intravesical infusion therapy is widely used to control recurrence after transurethral resection of bladder tumors. Herein, we report a case of polyneuropathy with transiently positive onconeural antibodies after BCG bladder infusion therapy. A man in his 70s presented with upper and lower extremity weakness 11 weeks after BCG intravesical infusion therapy, a postoperative therapy for superficial bladder cancer. Nerve conduction studies revealed findings that were consistent with demyelinating sensorimotor polyneuropathy. Anti-CV2 antibody was positive; however, contrast-enhanced computed tomography and positron emission tomography revealed no malignancy. The patient's symptoms improved with immunoglobulin therapy. Contrast-enhanced computed tomography showed no malignancy, and the anti-CV-2 antibody test result was negative six months after discharge. The immune response to BCG bladder infusion therapy may have caused the transient CV2 antibody positivity and polyneuropathy. The possibility of transiently positive onconeural antibodies after BCG intravesical infusion therapy should be considered.
Keywords: immunotherapy; neurology; peripheral neuropathies; urinary bladder neoplasms; vaccination.
Copyright © 2024, Saito et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[A Case Diagnosed as Iatrogenic Vesical Tuberculosis 4 Years after Intravesical Immunotherapy Using Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) for the Treatment of Bladder Carcinoma].Kansenshogaku Zasshi. 2016 Nov;90(6):809-13. Kansenshogaku Zasshi. 2016. PMID: 30277373 Japanese.
-
Renal Tuberculosis Following Intravesical Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) Immunotherapy for the Treatment of Bladder Cancer.Med Arch. 2020 Apr;74(2):146-150. doi: 10.5455/medarh.2020.74.146-150. Med Arch. 2020. PMID: 32577059 Free PMC article.
-
Intravesical Therapy for the Treatment of Nonmuscle Invasive Bladder Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Urol. 2017 May;197(5):1189-1199. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2016.12.090. Epub 2016 Dec 24. J Urol. 2017. PMID: 28027868
-
Intravesical versus intravesical plus intradermal bacillus Calmette-Guerin: a prospective randomized study in patients with recurrent superficial bladder tumors.J Urol. 1996 Feb;155(2):483-7. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(01)66427-9. J Urol. 1996. PMID: 8558641 Clinical Trial.
-
Diagnosis and management of superficial bladder cancer.Curr Probl Cancer. 2001 Jul-Aug;25(4):219-78. doi: 10.1067/mcn.2001.117539. Curr Probl Cancer. 2001. PMID: 11514784 Review.
References
-
- EAU guidelines on non-muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma of the bladder: update 2016. Babjuk M, Böhle A, Burger M, et al. Eur Urol. 2017;71:447–461. - PubMed
-
- Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) infection following intravesical BCG administration as adjunctive therapy for bladder cancer: incidence, risk factors, and outcome in a single-institution series and review of the literature. Pérez-Jacoiste Asín MA, Fernández-Ruiz M, López-Medrano F, et al. Medicine (Baltimore) 2014;93:236–254. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources