Efficacy and safety evaluation of first-line systemic treatments for unresectable esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: a network meta-analysis
- PMID: 39314629
- PMCID: PMC11416913
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1397960
Efficacy and safety evaluation of first-line systemic treatments for unresectable esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: a network meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the efficacy and safety of various first-line initial treatment systemic regimens for patients with unresectable esophageal squamous carcinoma(ESCC), utilizing a network meta-analysis approach.
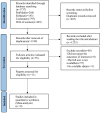
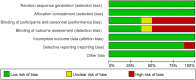
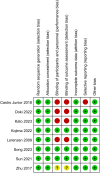
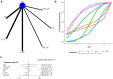
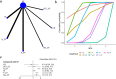
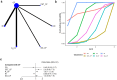
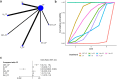
Methods: A comprehensive search for randomized controlled trials focusing on the primary treatment of esophageal cancer ESCC was conducted across multiple databases including PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, and Web of Science, up until November 17, 2023. The quality of the included studies was rigorously assessed using Review Manager software. Subsequently, data analysis was meticulously carried out employing R software. The first-line treatment regimens examined were: CD (Cisplatin + Docetaxel), CET-CF (Cetuximab + Cisplatin + Fluorouracil), CF (Cisplatin + Fluorouracil), N-CF (Nivolumab + Cisplatin + Fluorouracil), NI (Nivolumab + Ipilimumab), Nim-CF (Nimotuzumab + Cisplatin + Fluorouracil), P-CF (Pembrolizumab + Cisplatin + Fluorouracil), and Ser-CF (Serplulimab + Cisplatin + Fluorouracil). The Primary endpoints included the overall survival(OS),progression-free survival (PFS),objective response rate (ORR) and disease control rate (DCR).The secondary endpoint was adverse effects(AEs).
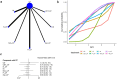
Results: The analysis encompassed eight studies, incorporating a total of 3,051 patients with untreated esophageal cancer. There are 45 people in the CD regimen,32 in the CET-CF regimen,1,212 in the CF regimen,447 in the N-CF regimen,456 in the NI regimen,53 in the Nim-CF regimen,447 in the P-CF regimen and 368 in the Ser-CF regimen. The network meta-analysis revealed that, in comparison to the CF regimen, the other regimens (CD, CET-CF, N-CF, NI, Nim-CF, P-CF, and Ser-CF) did not demonstrate a statistically significant impact on overall survival (OS) or progression-free survival (PFS). However, Ser-CF potentially offers superior outcomes in terms of OS and PFS when juxtaposed with other regimens. Notably, N-CF was associated with a substantial increase in the objective response rate (ORR), and CET-CF markedly improved the disease control rate (DCR). In terms of adverse effects, N-CF was more likely to cause anorexia, whereas CET-CF was significantly associated with nausea, vomiting, neutropenia, and skin disorders.
Conclusion: The current evidence suggests that N-CF may provide the most favorable outcomes in terms of ORR, while CET-CF could be the optimal choice for enhancing DCR in patients with untreated esophageal cancer.
Keywords: advanced esophageal squamous carcinoma; efficacy; first-line systemic treatments for esophageal cancer first-line treatment; network meta-analysis; safety.
Copyright © 2024 Shi, Tan, Ma, Wei, Shi, Wang, Xu and Liang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Docetaxel, cisplatin, and 5-fluorouracil compared with epirubicin, cisplatin, and 5-fluorouracil regimen for advanced gastric cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.World J Clin Cases. 2019 Mar 6;7(5):600-615. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i5.600. World J Clin Cases. 2019. PMID: 30863759 Free PMC article.
-
Nimotuzumab plus paclitaxel and cisplatin as the first line treatment for advanced esophageal squamous cell cancer: A single centre prospective phase II trial.Cancer Sci. 2016 Apr;107(4):486-90. doi: 10.1111/cas.12894. Epub 2016 Mar 28. Cancer Sci. 2016. PMID: 26797530 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Randomized multicenter phase III study of a modified docetaxel and cisplatin plus fluorouracil regimen compared with cisplatin and fluorouracil as first-line therapy for advanced or locally recurrent gastric cancer.Gastric Cancer. 2016 Jan;19(1):234-44. doi: 10.1007/s10120-015-0457-4. Epub 2015 Jan 21. Gastric Cancer. 2016. PMID: 25604851 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical efficacy of combination therapy of an immune checkpoint inhibitor with taxane plus platinum versus an immune checkpoint inhibitor with fluorouracil plus platinum in the first-line treatment of patients with locally advanced, metastatic, or recurrent esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2022 Dec 20;12:1015302. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1015302. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36605427 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the efficacy and safety of first-line treatments for of advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer in Asian populations: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jul 6;14:1212313. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1212313. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37484016 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rogers JE, Yamashita K, Sewastjanow-Silva M, Rosa Vicentini E, Waters R, Ajani JA. Nivolumab combination therapy as first-line treatments for unresectable, advanced or metastatic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. (2023) 23:565–71. doi: 10.1080/14737140.2023.2207826 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

