The application of lung immune prognostic index in predicting the prognosis of 302 STS patients
- PMID: 39314631
- PMCID: PMC11417100
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1460600
The application of lung immune prognostic index in predicting the prognosis of 302 STS patients
Abstract
Background: Soft tissue sarcoma (STS) are heterogeneous and rare tumors, and few studies have explored predicting the prognosis of patients with STS. The Lung Immune Prognostic Index (LIPI), calculated based on baseline serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and the derived neutrophils/(leukocytes minus neutrophils) ratio (dNLR), was considered effective in predicting the prognosis of patients with pulmonary cancer and other malignancies. However, the efficacy of the LIPI in predicting the prognosis of patients with STS remains unclear.
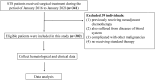
Methods: This study retrospectively reviewed patients with STS admitted to our center from January 2016 to January 2021. Their hematological and clinical characteristics were collected and analyzed to construct the LIPI specific to STS. The correlations between various predictive factors and overall survival (OS) were examined using Kaplan-Meier and Cox regression analyses. Independent risk factors for OS were identified using univariate and multivariate analyses. Finally, a LIPI nomogram model for STS was established.
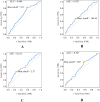
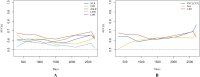
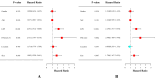
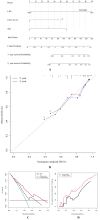
Results: This study enrolled 302 patients with STS, of which 87 (28.9%), 162 (53.6%), and 53 (17.5%) were classified into three LIPI-based categories: good, moderate, and poor, respectively (P < 0.0001). The time-dependent operator curve showed that the LIPI had better prognostic predictive ability than other hematological and clinical characteristics. Univariate and multivariate analyses identified the Fédération Nationale des Centres de Lutte Contre le Cancer grade (FNCLCC/G), tumor size, and LIPI as independent risk factors. Finally, a nomogram was constructed by integrating the significant prognostic factors. Its C-index was 0.72, and the calibration curve indicated that it could accurately predict the three- and five-year OS of patients with STS. The decision and clinical impact curves also indicated that implementing this LIPI-nomogram could significantly benefit patients with STS.
Conclusion: This study explored the efficacy of the LIPI in predicting the prognosis of 302 patients with STS, classifying them into three categories to evaluate the prognosis. It also reconstructed a LIPI-based nomogram to assist clinicians in predicting the three- and five-year OS of patients with STS, potentially enabling timely intervention and customized management.
Keywords: derived neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (dNLR); lactate dehydrogenase (LDH); lung immune prognostic index (LIPI); prognosis; soft tissue sarcoma.
Copyright © 2024 Jiang, Zou, He, Li, Luo, Lu, Li, Gong, Wang, Min, Zhou and Tu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Lung Immune Prognostic Index Could Predict Metastasis in Patients With Osteosarcoma.Front Surg. 2022 Jul 8;9:923427. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.923427. eCollection 2022. Front Surg. 2022. PMID: 35874141 Free PMC article.
-
[Effect of dNLR and LIPI scores on the prognosis of elderly patients with non-surgical treatment of non-small cell lung cancer].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2022 Sep 23;44(9):975-980. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112152-20200423-00371. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 36164700 Chinese.
-
Prognostic significance of modified lung immune prognostic index in osteosarcoma patients.Front Genet. 2022 Oct 11;13:972352. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.972352. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36303539 Free PMC article.
-
Prognosis stratification of cancer patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors through lung immune prognostic index: a meta-analysis and systematic review.BMC Cancer. 2024 Apr 25;24(1):523. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12271-0. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38664760 Free PMC article.
-
The Predictive Value of Pretreatment Lactate Dehydrogenase and Derived Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients Treated With PD-1/PD-L1 Inhibitors: A Meta-Analysis.Front Oncol. 2022 Jul 18;12:791496. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.791496. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35924149 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Development of a lung immune prognostic index-based nomogram model for predicting overall survival and immune-related adverse events in non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with sintilimab.Front Immunol. 2025 May 8;16:1569689. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1569689. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40406139 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gronchi A, Palmerini E, Quagliuolo V, Martin Broto J, Lopez Pousa A, Grignani G, et al. . Neoadjuvant chemotherapy in high-risk soft tissue sarcomas: final results of a randomized trial from Italian (ISG), Spanish (GEIS), French (FSG), and Polish (PSG) Sarcoma Groups. J Clin Oncol. (2020) 38:2178–86. doi: 10.1200/jco.19.03289 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

