Hybrid computing framework security in dynamic offloading for IoT-enabled smart home system
- PMID: 39314732
- PMCID: PMC11419611
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj-cs.2211
Hybrid computing framework security in dynamic offloading for IoT-enabled smart home system
Abstract
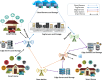
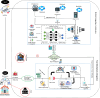
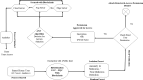
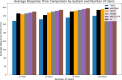
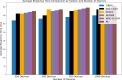
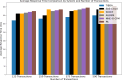
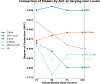
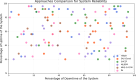
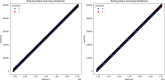
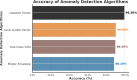
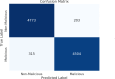
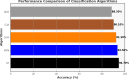
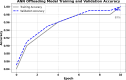
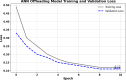
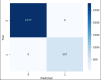
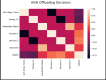
In the distributed computing era, cloud computing has completely changed organizational operations by facilitating simple access to resources. However, the rapid development of the IoT has led to collaborative computing, which raises scalability and security challenges. To fully realize the potential of the Internet of Things (IoT) in smart home technologies, there is still a need for strong data security solutions, which are essential in dynamic offloading in conjunction with edge, fog, and cloud computing. This research on smart home challenges covers in-depth examinations of data security, privacy, processing speed, storage capacity restrictions, and analytics inside networked IoT devices. We introduce the Trusted IoT Big Data Analytics (TIBDA) framework as a comprehensive solution to reshape smart living. Our primary focus is mitigating pervasive data security and privacy issues. TIBDA incorporates robust trust mechanisms, prioritizing data privacy and reliability for secure processing and user information confidentiality within the smart home environment. We achieve this by employing a hybrid cryptosystem that combines Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC), Post Quantum Cryptography (PQC), and Blockchain technology (BCT) to protect user privacy and confidentiality. Additionally, we comprehensively compared four prominent Artificial Intelligence anomaly detection algorithms (Isolation Forest, Local Outlier Factor, One-Class SVM, and Elliptic Envelope). We utilized machine learning classification algorithms (random forest, k-nearest neighbors, support vector machines, linear discriminant analysis, and quadratic discriminant analysis) for detecting malicious and non-malicious activities in smart home systems. Furthermore, the main part of the research is with the help of an artificial neural network (ANN) dynamic algorithm; the TIBDA framework designs a hybrid computing system that integrates edge, fog, and cloud architecture and efficiently supports numerous users while processing data from IoT devices in real-time. The analysis shows that TIBDA outperforms these systems significantly across various metrics. In terms of response time, TIBDA demonstrated a reduction of 10-20% compared to the other systems under varying user loads, device counts, and transaction volumes. Regarding security, TIBDA's AUC values were consistently higher by 5-15%, indicating superior protection against threats. Additionally, TIBDA exhibited the highest trustworthiness with an uptime percentage 10-12% greater than its competitors. TIBDA's Isolation Forest algorithm achieved an accuracy of 99.30%, and the random forest algorithm achieved an accuracy of 94.70%, outperforming other methods by 8-11%. Furthermore, our ANN-based offloading decision-making model achieved a validation accuracy of 99% and reduced loss to 0.11, demonstrating significant improvements in resource utilization and system performance.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Big data; Blockchain; Cryptography; Data security and privacy; Hybrid computing; Internet of Things (IoT); Machine learning; Offloading; Smart home.
©2024 Khan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Abbas K, Tawalbeh LA, Rafiq A, Muthanna A, Elgendy IA, Abd El-Latif AA. Convergence of blockchain and IoT for secure transportation systems in smart cities. Security and Communication Networks. 2021;2021:1–13. doi: 10.1155/2021/5597679. - DOI
-
- Achar S. Cloud computing security for multi-cloud service providers: controls and techniques in our modern threat landscape. International Journal of Computer and Systems Engineering. 2022;16(9):379–384.
-
- Ahanger TA, Tariq U, Ibrahim A, Ullah I, Bouteraa Y. Iot-inspired framework of intruder detection for smart home security systems. Electronics. 2020;9(9):1361. doi: 10.3390/electronics9091361. - DOI
-
- Ahmad S, Mehfuz S, Beg J. Hybrid cryptographic approach to enhance the mode of key management system in cloud environment. The Journal of Supercomputing. 2023;79(7):7377–7413. doi: 10.1007/s11227-022-04964-9. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
