Circulating extracellular vesicles as biomarkers in the diagnosis, prognosis and therapy of cardiovascular diseases
- PMID: 39314768
- PMCID: PMC11417624
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1425159
Circulating extracellular vesicles as biomarkers in the diagnosis, prognosis and therapy of cardiovascular diseases
Abstract
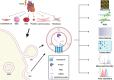
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) ranks among the primary contributors to worldwide mortality. Hence, the importance of constant research on new circulating biomarkers for the improvement of early diagnosis and prognostication of different CVDs and the development and refinement of therapeutic measures is critical. Extracellular vesicles (EV) have a great potential as diagnostic and prognostic markers, as they represent their parent cell by enclosing cell-specific molecules, which can differ in quality and quantity based on cell state. Assuming that all cell types of the cardiovascular system are capable of releasing EV into circulation, an emerging body of evidence has investigated the potential role of serum- or plasma-derived EV in CVD. Comprehensive research has unveiled alterations in EV quantity and EV-bound cargo in the form of RNA, proteins and lipids in the context of common CVDs such as coronary artery disease, atrial fibrillation, heart failure or inflammatory heart diseases, highlighting their diagnostic and prognostic relevance. In numerous in vitro and in vivo models, EV also showed promising therapeutic potential. However, translation of EV studies to a preclinical or clinical setting has proven to be challenging. This review is intended to provide an overview of the most relevant studies in the field of serum or plasma-derived EV.
Keywords: biomarker; cardiovascular disease; diagnosis; extracellular vesicles; prognosis; therapy.
© 2024 Bernáth-Nagy, Kalinyaprak, Giannitsis, Ábrahám, Leuschner, Frey and Krohn.
Conflict of interest statement
JBK received project-related funding by Roche Diagnostics. EG received honoraria for lectures from Roche Diagnostics, BRAHMS Thermo Scientific, Bayer Vital GmbH, Lilly Deutschland, Boehringer Ingelheim, AstraZeneca, institutional research grant from Roche Diagnostics and Daiichi Sankyo, consultant for Roche Diagnostics and BRAHMS Thermo Scientific, Boehringer Ingelheim outside the submitted work. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

