Raw meat diets are a major risk factor for carriage of third-generation cephalosporin-resistant and multidrug-resistant E. coli by dogs in the UK
- PMID: 39314877
- PMCID: PMC11417003
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1460143
Raw meat diets are a major risk factor for carriage of third-generation cephalosporin-resistant and multidrug-resistant E. coli by dogs in the UK
Abstract
Introduction: Raw-meat diets (RMD) for dogs, comprising unprocessed or non-heat-treated animal material, are increasingly popular. However, RMDs have been demonstrated to be contaminated with antimicrobial resistant (AMR) bacteria, and there is concern that such diets may pose a zoonotic disease risk. Additionally, dogs fed RMD may shed more AMR- fecal bacteria compared to those fed conventional cooked diets. Data from the UK remain limited; the present study investigated the presence of AMR-Escherichia coli in the feces of RMD and non-RMD (NRMD)-fed dogs in the UK, the E. coli AMR gene complement, and the lifestyle risk factors associated with AMR- E. coli carriage.
Methods: Fecal samples from UK-owned dogs (N = 193 RMD, N = 239 NRMD) and questionnaires discussing lifestyle factors, were obtained between October 2020-August 2021. Samples underwent culture and antimicrobial susceptibility testing to determine the presence of AMR-E. coli. Whole genome sequencing determined AMR gene carriage. Risk factors for the presence of AMR-E. coli were determined by multivariable modeling.
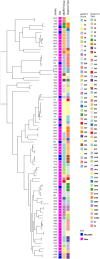
Results: RMD dogs carried significantly more fecal AMR E. coli (p < 0.001), including third-generation cephalosporin resistant, extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL) producing, and multidrug resistant isolates and multivariable modeling confirmed raw-meat diets to be a significant risk factor. The bla CTX-M-15 gene was the most frequently identified bla ESBL gene. The bla CTX-M-55 and bla SHV-66 genes were also prevalent and were only found in RMD dogs. The mobile colistin resistance gene, mcr-4 was identified in one ESBL-producing E. coli isolate from a NRMD-fed dog.
Conclusion: This study has shown that dogs fed RMD in the UK are significantly more likely to shed E. coli which is resistant to highest priority critically important antibiotics, and multidrug resistant E. coli, than dogs fed NRMD. Additionally, AMR-E. coli isolates from RMD-fed dogs harbor multiple, diverse, and novel AMR genes. Therefore, provision of RMD to dogs could pose an important potential threat to human and animal health, especially given the close nature of the relationship many owners share with their pets. Awareness of these findings should be shared with pet owners, veterinary and medical professionals, pet food manufacturers and public health to mitigate potential risks.
Keywords: AMR; E. coli; One Health; carriage; dog; raw meat diet.
Copyright © 2024 Morgan, Pinchbeck, Haldenby, Schmidt and Williams.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
An investigation of the presence and antimicrobial susceptibility of Enterobacteriaceae in raw and cooked kibble diets for dogs in the United Kingdom.Front Microbiol. 2024 Jan 8;14:1301841. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1301841. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38260907 Free PMC article.
-
A Dog's Dinner: Factors affecting food choice and feeding practices for UK dog owners feeding raw meat-based or conventional cooked diets.Prev Vet Med. 2022 Nov;208:105741. doi: 10.1016/j.prevetmed.2022.105741. Epub 2022 Aug 9. Prev Vet Med. 2022. PMID: 35994979
-
Genomic profiling of extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli from Pets in the United Arab Emirates: Unveiling colistin resistance mediated by mcr-1.1 and its probable transmission from chicken meat - A One Health perspective.J Infect Public Health. 2023 Dec;16 Suppl 1:163-171. doi: 10.1016/j.jiph.2023.10.034. Epub 2023 Nov 3. J Infect Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37957104
-
Global Distribution of Extended Spectrum Cephalosporin and Carbapenem Resistance and Associated Resistance Markers in Escherichia coli of Swine Origin - A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Microbiol. 2022 May 10;13:853810. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.853810. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35620091 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Risk factors for antimicrobial-resistant Enterobacterales in dogs: a systematic review.Front Vet Sci. 2024 Oct 7;11:1447707. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1447707. eCollection 2024. Front Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 39439826 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Dogs fed raw meat-based diets are vectors of drug-resistant Salmonella infection in humans.Commun Med (Lond). 2025 Jun 4;5(1):214. doi: 10.1038/s43856-025-00919-2. Commun Med (Lond). 2025. PMID: 40467866 Free PMC article.
-
The Risk Factors Associated with the Carriage to Critical Antimicrobial-Resistant Escherichia coli in Healthy Household Dogs: A One Health Perspective.Animals (Basel). 2025 May 8;15(10):1357. doi: 10.3390/ani15101357. Animals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40427235 Free PMC article.
-
Application of Behavior Change Techniques (BCTTv1) to Reduce Antimicrobial Use in Livestock: A Scoping Review.Vet Sci. 2025 Feb 14;12(2):172. doi: 10.3390/vetsci12020172. Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40005932 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anastasi E., Matthews B., Gundogdu A., Vollmerhausen T., Ramos N., Stratton H., et al. (2010). Prevalence and persistence of Escherichia coli strains with uropathogenic virulence characteristics in sewage treatment plants. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 76 5882–5886. 10.1128/AEM.00141-10 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

