Understanding the impact of radiation-induced lymphopenia: Preclinical and clinical research perspectives
- PMID: 39315059
- PMCID: PMC11418132
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ctro.2024.100852
Understanding the impact of radiation-induced lymphopenia: Preclinical and clinical research perspectives
Abstract
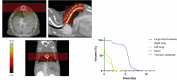
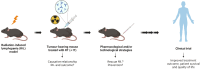
Immunotherapy has revolutionized the field of cancer treatment, changing the standard of care to the use of immune checkpoint inhibitors. Radiotherapy can boost anti-tumour immune responses by changing the tumour microenvironment, but it also can cause radiotherapy-induced lymphopenia (RIL), a decrease in circulating lymphocyte counts. RIL has been associated with lower survival in patients undergoing radiotherapy, and new studies have suggested that it can also affect immunotherapy outcome. To study RIL's effects and to explore mitigation treatment strategies, preclinical models closely mimicking the clinical situation are needed. State-of-the-art image-guided small animal irradiators now offer the possibility to target specific organs in small animals to induce RIL, aiding research on its molecular mechanisms and prevention. This review covers the relationship between radiotherapy and RIL, its impact on patient survival, and future directions to generate models to investigate and prevent RIL.
Keywords: Immunotherapy; Preclinical models; Radiation-induced lymphopenia.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: L.J.D. has, outside of the submitted work, shares in the companies Convert Pharmaceuticals and LivingMed Biotech, he is co-inventor of a non-issued patent on LSRT (N2024889). The other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Lesterhuis W.J., Haanen J.B.A.G., Punt C.J.A. Cancer immunotherapy – revisited. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2011;10(8):591–600. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

