Causal effects of systemic inflammatory proteins on Guillain-Barre Syndrome: insights from genome-wide Mendelian randomization, single-cell RNA sequencing analysis, and network pharmacology
- PMID: 39315093
- PMCID: PMC11416972
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1456663
Causal effects of systemic inflammatory proteins on Guillain-Barre Syndrome: insights from genome-wide Mendelian randomization, single-cell RNA sequencing analysis, and network pharmacology
Abstract
Background: Evidence from observational studies indicates that inflammatory proteins play a vital role in Guillain-Barre Syndrome (GBS). Nevertheless, it is unclear how circulating inflammatory proteins are causally associated with GBS. Herein, we conducted a two-sample Mendelian randomization (MR) analysis to systematically explore the causal links of genetically determined systemic inflammatory proteins on GBS.
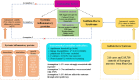
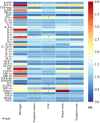
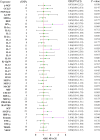
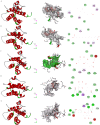
Methods: A total of 8,293 participants of European ancestry were included in a genome-wide association study of 41 inflammatory proteins as instrumental variables. Five MR approaches, encompassing inverse-variance weighted, weighted median, MR-Egger, simple model, and weighted model were employed to explore the causal links between inflammatory proteins and GBS. MR-Egger regression was utilized to explore the pleiotropy. Cochran's Q statistic was implemented to quantify the heterogeneity. Furthermore, we performed single-cell RNA sequencing analysis and predicted potential drug targets through molecular docking technology.
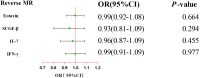
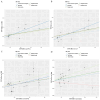
Results: By applying MR analysis, four inflammatory proteins causally associated with GBS were identified, encompassing IFN-γ (OR:1.96, 95%CI: 1.02-3.78, PIVW=0.045), IL-7 (OR:1.86, 95%CI: 1.07-3.23, PIVW=0.029), SCGF-β (OR:1.56, 95%CI: 1.11-2.19, PIVW=0.011), and Eotaxin (OR:1.99, 95%CI: 1.01-3.90, PIVW=0.046). The sensitivity analysis revealed no evidence of pleiotropy or heterogeneity. Additionally, significant genes were found through single-cell RNA sequencing analysis and several anti-inflammatory or neuroprotective small molecular compounds were identified by utilizing molecular docking technology.
Conclusions: Our MR analysis suggested that IFN-γ, IL-7, SCGF-β, and Eotaxin were causally linked to the occurrence and development of GBS. These findings elucidated potential causal associations and highlighted the significance of these inflammatory proteins in the pathogenesis and prospective therapeutic targets for GBS.
Keywords: Guillain-Barre Syndrome; Mendelian randomization; molecular docking; single-cell RNA-seq; systemic inflammatory proteins.
Copyright © 2024 Liu and Pan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Causal links of human serum metabolites on the risk of prostate cancer: insights from genome-wide Mendelian randomization, single-cell RNA sequencing, and metabolic pathway analysis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Nov 12;15:1443330. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1443330. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39600951 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between Guillain-Barré syndrome and cardiovascular disease: a bidirectional Mendelian randomization study.Physiol Genomics. 2025 Feb 1;57(2):80-90. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00048.2024. Epub 2024 Oct 28. Physiol Genomics. 2025. PMID: 39466182
-
Explore genetic susceptibility association between viral infections and Guillain-Barré syndrome risk using two-sample Mendelian randomization.J Transl Med. 2024 Oct 2;22(1):890. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05704-8. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39358724 Free PMC article.
-
[Genetic Causation Analysis of Hyperandrogenemia Testing Indicators and Preeclampsia].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024 May 20;55(3):566-573. doi: 10.12182/20240560106. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024. PMID: 38948277 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Genetic Architecture of Neurological Disorders and Their Endophenotypes: Insights from Genetic Association Studies.Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2024;68:109-128. doi: 10.1007/7854_2024_513. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39138743 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical and electrophysiological features of pure sensory Guillain-Barré syndrome: retrospective analysis of 22 patients across 14 provinces in Southern China.BMC Neurol. 2025 Mar 6;25(1):87. doi: 10.1186/s12883-025-04103-w. BMC Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40050755 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

