Network pharmacology and bioinformatics approach to unravel the mechanism of Xiao-chai-hu-tang herbal formula in tinnitus treatment
- PMID: 39315211
- PMCID: PMC11417242
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37584
Network pharmacology and bioinformatics approach to unravel the mechanism of Xiao-chai-hu-tang herbal formula in tinnitus treatment
Abstract
Background: Tinnitus treatment remains a global challenge, and current therapeutic approaches are still controversial. This study aims to elucidate the potential mechanisms of Xiao-Chai-Hu-Tang (XCHT) in treating tinnitus through the analysis of network pharmacology, mendelian randomization and molecular docking, and molecular dynamics simulation analysis. We hope to contribute to the research on the target of action of traditional Chinese medicine and exploration of the mechanism of tinnitus.
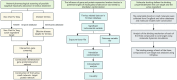
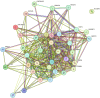
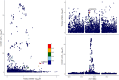
Methods: We utilized network pharmacology to screen potential targets of action of XCHT on tinnitus. Mendelian randomization was employed to determine the causal relationship between potential targets of action and tinnitus. Finally, molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulation with clear targets and the combination of the active ingredient in effectiveness.
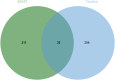
Results: Through network pharmacology, we identified 38 potential targets of action. Mendelian randomization analysis revealed that HIF1A (OR [95 % CI] = 0.78 [0.65, 0.94], P = 0.008) and CCND1 (OR [95 % CI] = 1.22 [1.00, 1.49], P = 0.04) exhibited significant results with tinnitus. Molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulation of HIF1A and active ingredients demonstrated good binding efficacy.
Conclusion: HIF1A may play a key role in the treatment of tinnitus by XCHT, which may play a certain protective role in tinnitus patients and may inhibit the occurrence and development of tinnitus. However, the specific mechanism and effect need to be further studied and verified.
Keywords: HIF1A; Mendelian randomization; Molecular docking; Network pharmacology; Tinnitus; Xiao-chai-hu-tang.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Network pharmacology and molecular docking study on the mechanism of colorectal cancer treatment using Xiao-Chai-Hu-Tang.PLoS One. 2021 Jun 14;16(6):e0252508. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0252508. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34125845 Free PMC article.
-
Xiao-Chai-Hu-Tang Ameliorates Depressive Symptoms via Modulating Neuro-Endocrine Network in Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress-Induced Mice.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025 Feb;31(2):e70290. doi: 10.1111/cns.70290. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025. PMID: 39981856 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding the polypharmacological anticancer effects of Xiao Chai Hu Tang via a computational pharmacological model.Exp Ther Med. 2014 Jun;7(6):1777-1783. doi: 10.3892/etm.2014.1660. Epub 2014 Apr 2. Exp Ther Med. 2014. PMID: 24926384 Free PMC article.
-
Xiao Chai Hu Tang, a herbal medicine, for chronic hepatitis B.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Nov 7;2019(11):CD013090. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013090.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31697415 Free PMC article.
-
Xiao Chai Hu Tang for Peptic Ulcers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Apr 29;2021:6693677. doi: 10.1155/2021/6693677. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 34012475 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Warfarin use and vestibular dysfunction insights from NHANES data, network pharmacology, Mendelian randomization, and molecular docking.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 6;15(1):11748. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-96681-5. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40189685 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dalrymple S.N., Lewis S.H., Philman S. Tinnitus: diagnosis and management. Am. Fam. Physician. 2021;103(11):663–671. - PubMed
-
- Langguth B., Kreuzer P.M., Kleinjung T., De Ridder D. Tinnitus: causes and clinical management. Lancet Neurol. 2013;12(9):920–930. - PubMed
-
- Baguley D., McFerran D., Hall D. Tinnitus. Lancet. 2013;382(9904):1600–1607. - PubMed
-
- Yu S., Wu J., Sun Y., Lyu J. Advances in acupuncture treatment for tinnitus. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2024;45(3) - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

