Ultrasound-assisted extraction of polysaccharides from Ginkgo biloba: Process optimization, composition and anti-inflammatory activity
- PMID: 39315214
- PMCID: PMC11417318
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37811
Ultrasound-assisted extraction of polysaccharides from Ginkgo biloba: Process optimization, composition and anti-inflammatory activity
Abstract
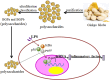
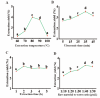
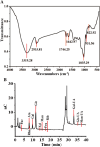
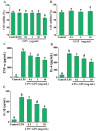
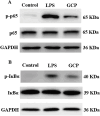
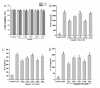
Plant derived polysaccharides can enhance immune function in the human body, effectively prevent diseases, and reduce the probability of bacterial infections. Ginkgo crude polysaccharide (GCP) was obtained from Ginkgo biloba by ultrasonic-assisted hot water extraction. Our data showed that the best extraction conditions of GCP were as follows: extraction temperature 80 °C, ultrasonic time 35 min, extraction time 3 h, and solid‒liquid ratio 1:30. Fourier transform infrared spectrometer (FT-IR) data showed that this polysaccharide might be an acidic polysaccharide with a carboxylic acid ring structure. Further studies implied that GCP was mainly composed of glucose, galacturonic acid, rhamnose, galactose and arabinose, accounting for 39.45 %, 25.01 %, 15.40 %, 11.94 % and 4.25 %, respectively. 0.1, 1 and 10 mg/mL GCP reduced the release of inflammatory factors in RAW264.7 cells via inhibition of the nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B (NF-κB) signalling pathway. GCP was separated into five components with different molecular weights by an ultrafiltration membrane. Our data showed that GPa with a molecular weight ≥100 kDa was the main component of GCP. 1 mg/mL GPa, GPb, GPc and GPd had anti-inflammatory activities, and 1 mg/mL GPa had the best anti-inflammatory activities. Our results preliminarily reveal the elements and biological activity of GCP, which will provide a reference for the development of Ginkgo biloba.
Keywords: Ginkgo biloba; Inflammatory factors; Ultrafiltration membrane.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests:Yanyang Wu reports financial support was provided by 10.13039/100014717National Natural Science Foundation of China. If there are other authors, they declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Characterization and antioxidant activity of Ginkgo biloba exocarp polysaccharides.Carbohydr Polym. 2012 Jan 4;87(1):40-45. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.06.083. Epub 2011 Aug 5. Carbohydr Polym. 2012. PMID: 34662981
-
Ultrasound-assisted extraction and properties of polysaccharide from Ginkgo biloba leaves.Ultrason Sonochem. 2023 Feb;93:106295. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2023.106295. Epub 2023 Jan 10. Ultrason Sonochem. 2023. PMID: 36638652 Free PMC article.
-
[The purification and characterization of polysaccharides isolated from Ginkgo biloba and their in vitro antioxidant activities].Zhong Yao Cai. 2011 Dec;34(12):1950-3. Zhong Yao Cai. 2011. PMID: 22500437 Chinese.
-
Extraction, structure and bioactivities of the polysaccharides from Ginkgo biloba: A review.Int J Biol Macromol. 2020 Nov 1;162:1897-1905. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.08.141. Epub 2020 Aug 19. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020. PMID: 32827622 Review.
-
Advances in Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Extraction of Bioactive Substances from Different Parts of Ginkgo biloba L.Molecules. 2021 Jun 30;26(13):4011. doi: 10.3390/molecules26134011. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34209219 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ultrasound-assisted extraction, optimization, characteristics and antioxidant activity of Piper nigrum L. polysaccharides.Ultrason Sonochem. 2025 May;116:107309. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2025.107309. Epub 2025 Mar 13. Ultrason Sonochem. 2025. PMID: 40101530 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen Y., Fu C., Wu Z., Xu H., Liu H., Schneider H., Lin J. Ginkgo biloba. Trends Genet. : TIG (Trends Genet.) 2021;37:488–489. http://10.1016/j.tig.2021.01.009 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Biernacka P., Adamska I., Felisiak K. The potential of ginkgo biloba as a source of biologically active compounds-A review of the recent literature and patents. Molecules. 2023;28:3993. http://10.3390/Molecules28103993 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boateng I.D. Polyprenols in Ginkgo biloba; a review of their chemistry (synthesis of polyprenols and their derivatives), extraction, purification, and bioactivities. Food Chem. 2023;418 http://10.1016/j.foodchem.2023.136006 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Li J., Chen Z., Shi H., Yu J., Huang G., Huang H. Ultrasound-assisted extraction and properties of polysaccharide from Ginkgo biloba leaves. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2023;93 http://10.1016/j.ultsonch.2023.106295 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Liu Y., Xin H., Zhang Y., Che F., Shen N., Cui Y. Leaves, seeds and exocarp of Ginkgo biloba L. (Ginkgoaceae): a Comprehensive Review of Traditional Uses, phytochemistry, pharmacology, resource utilization and toxicity. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022;298 http://10.1016/j.jep.2022.115645 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

