Investigation of Zur-regulated metal transport systems reveals an unexpected role of pyochelin in zinc homeostasis
- PMID: 39315802
- PMCID: PMC11481552
- DOI: 10.1128/mbio.02395-24
Investigation of Zur-regulated metal transport systems reveals an unexpected role of pyochelin in zinc homeostasis
Abstract
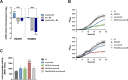
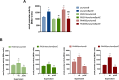
Limiting the availability of transition metals at infection sites serves as a critical defense mechanism employed by the innate immune system to combat microbial infections. Pseudomonas aeruginosa exhibits a remarkable ability to thrive in zinc-deficient environments, facilitated by intricate cellular responses governed by numerous genes regulated by the zinc-responsive transcription factor Zur. Many of these genes have unknown functions, including those within the predicted PA2911-PA2914 and PA4063-PA4066 operons. A structural bioinformatics investigation revealed that PA2911-PA2914 comprises a TonB-dependent outer membrane receptor and inner membrane ABC-permeases responsible for importing metal-chelating molecules, whereas PA4063-PA4066 contains genes encoding a MacB transporter, likely involved in the export of large molecules. Molecular genetics and biochemical experiments, feeding assays, and intracellular metal content measurements support the hypothesis that PA2911-PA2914 and PA4063-PA4066 are engaged in the import and export of the pyochelin-cobalt complex, respectively. Notably, cobalt can reduce zinc demand and promote the growth of P. aeruginosa strains unable to import zinc, highlighting pyochelin-mediated cobalt import as a novel bacterial strategy to counteract zinc deficiency. These results unveil an unexpected role for pyochelin in zinc homeostasis and challenge the traditional view of this metallophore exclusively as an iron transporter.
Importance: The mechanisms underlying the remarkable ability of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to resist the zinc sequestration mechanisms implemented by the vertebrate innate immune system to control bacterial infections are still far from being fully understood. This study reveals that the Zur-regulated gene clusters PA2911-2914 and PA4063-PA4066 encode systems for the import and export of cobalt-bound pyochelin, respectively. This proves to be a useful strategy to counteract conditions of severe zinc deficiency since cobalt can replace zinc in many proteins. The discovery that pyochelin may contribute to cellular responses to zinc deficiency leads to a reevaluation of the paradigm that pyochelin is a siderophore involved exclusively in iron acquisition and suggests that this molecule has a broader role in modulating the homeostasis of multiple metals.
Keywords: Pseudomonas aeruginosa; cystic fibrosis; iron transport; metal transport; metallophore; siderophores; zinc transport; zincophores.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



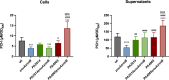




Similar articles
-
Inner-membrane transporters for the siderophores pyochelin in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and enantio-pyochelin in Pseudomonas fluorescens display different enantioselectivities.Microbiology (Reading). 2012 May;158(Pt 5):1317-1324. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.057430-0. Epub 2012 Feb 16. Microbiology (Reading). 2012. PMID: 22343350
-
Activation of CzcS/CzcR during zinc excess regulates copper tolerance and pyochelin biosynthesis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2024 Mar 20;90(3):e0232723. doi: 10.1128/aem.02327-23. Epub 2024 Feb 20. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38376236 Free PMC article.
-
Ferric Uptake Regulator Fur Is Conditionally Essential in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.J Bacteriol. 2017 Oct 17;199(22):e00472-17. doi: 10.1128/JB.00472-17. Print 2017 Nov 15. J Bacteriol. 2017. PMID: 28847923 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between Pyochelin and Pseudomonas Quinolone Signal in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: A Direction for Future Research.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 7;25(16):8611. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168611. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201297 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Zinc homeostasis in Pseudomonas.Biometals. 2023 Aug;36(4):729-744. doi: 10.1007/s10534-022-00475-5. Epub 2022 Dec 6. Biometals. 2023. PMID: 36472780 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Proteomic profiling of zinc homeostasis mechanisms in Pseudomonas aeruginosa through data-dependent and data-independent acquisition mass spectrometry.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jan 31:2025.01.13.632865. doi: 10.1101/2025.01.13.632865. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: Metallomics. 2025 Aug 5;17(8):mfaf020. doi: 10.1093/mtomcs/mfaf020. PMID: 39868216 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Modelling host-pathogen interactions: Galleria mellonella as a platform to study Pseudomonas aeruginosa response to host-imposed zinc starvation.Microbiology (Reading). 2025 Jan;171(1):001524. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.001524. Microbiology (Reading). 2025. PMID: 39841126 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
