Autoantibodies neutralizing type I IFNs underlie severe tick-borne encephalitis in ∼10% of patients
- PMID: 39316018
- PMCID: PMC11448868
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20240637
Autoantibodies neutralizing type I IFNs underlie severe tick-borne encephalitis in ∼10% of patients
Abstract
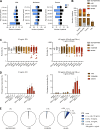
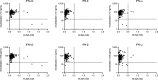
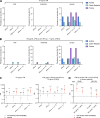
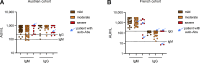
Tick-borne encephalitis (TBE) virus (TBEV) is transmitted to humans via tick bites. Infection is benign in >90% of the cases but can cause mild (<5%), moderate (<4%), or severe (<1%) encephalitis. We show here that ∼10% of patients hospitalized for severe TBE in cohorts from Austria, Czech Republic, and France carry auto-Abs neutralizing IFN-α2, -β, and/or -ω at the onset of disease, contrasting with only ∼1% of patients with moderate and mild TBE. These auto-Abs were found in two of eight patients who died and none of 13 with silent infection. The odds ratios (OR) for severe TBE in individuals with these auto-Abs relative to those without them in the general population were 4.9 (95% CI: 1.5-15.9, P < 0.0001) for the neutralization of only 100 pg/ml IFN-α2 and/or -ω, and 20.8 (95% CI: 4.5-97.4, P < 0.0001) for the neutralization of 10 ng/ml IFN-α2 and -ω. Auto-Abs neutralizing type I IFNs accounted for ∼10% of severe TBE cases in these three European cohorts.
© 2024 Gervais et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: The Center for Virology, Medical University of Vienna, Austria, received an Investigator-Initiated Research grant from Pfizer (WI235042), with J.H. Aberle as principal investigator, which is not related to the submitted work. J.-L. Casanova reported a patent to PCT/US2021/042741 pending. No other disclosures were reported.
Figures

References
-
- Ackermann-Gäumann, R., Eyer C., Vock M., Gowland P., Tinguely C., Leib S.L., Bori M., Buser A., Fontana S., Thierbach J., et al. . 2023. Prevalence of anti-tick-borne encephalitis virus (TBEV) antibodies in Swiss blood donors in 2014-2015. Blood Transfus. 21:100–109. 10.2450/2022.0099-22 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Agudelo, M., Palus M., Keeffe J.R., Bianchini F., Svoboda P., Salát J., Peace A., Gazumyan A., Cipolla M., Kapoor T., et al. . 2021. Broad and potent neutralizing human antibodies to tick-borne flaviviruses protect mice from disease. J. Exp. Med. 218:e20210236. 10.1084/jem.20210236 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alotaibi, F., Alharbi N.K., Rosen L.B., Asiri A.Y., Assiri A.M., Balkhy H.H., Al Jeraisy M., Mandourah Y., AlJohani S., Al Harbi S., et al. . 2023. Type I interferon autoantibodies in hospitalized patients with Middle East respiratory syndrome and association with outcomes and treatment effect of interferon beta-1b in MIRACLE clinical trial. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses. 17:e13116. 10.1111/irv.13116 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bastard, P., Gervais A., Le Voyer T., Rosain J., Philippot Q., Manry J., Michailidis E., Hoffmann H.H., Eto S., Garcia-Prat M., et al. . 2021a. Autoantibodies neutralizing type I IFNs are present in ∼4% of uninfected individuals over 70 years old and account for ∼20% of COVID-19 deaths. Sci. Immunol. 6:eabl4340. 10.1126/sciimmunol.abl4340 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- Strasbourg University
- EQU201903007798/French Foundation for Medical Research
- Rockefeller University
- Meyer Foundation
- European Union
- RC08061819/Italian Ministry of Health
- ANR-10-IAHU-01/Agence Nationale de la Recherche
- 08061821/San Matteo Hospital
- Imagine Institute
- R01 AI163029/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- LX22N-PO5103/National Institute of Virology and Bacteriology
- UL1 TR001866/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI124690/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- Battersea & Bowery Advisory Group
- R01AI163029/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- Grandir - Fonds de solidarité pour l'enfance
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- Square Foundation
- PRI 7782/Strasbourg University Hospital
- NU22-05-00659/Czech Ministry of Health
- Fondation du Souffle
- SCOR Corporate Foundation for Science
- St. Giles Foundation
- UMR_S 1109/Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale
- Bettencourt-Schueller Foundation
- PHRCN-17-0382/Ministry of Health
- Paris Cité University
- JPB Foundation
- MESRI-COVID-19/French Ministry of Higher Education, Research, and Innovation
- Stavros Niarchos Foundation
- Fisher Center for Alzheimer's Research Foundation
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

