Impact of COVID-19 on 2021 cancer incidence rates and potential rebound from 2020 decline
- PMID: 39316386
- PMCID: PMC11884841
- DOI: 10.1093/jnci/djae180
Impact of COVID-19 on 2021 cancer incidence rates and potential rebound from 2020 decline
Abstract
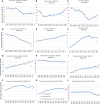
The COVID-19 pandemic led to substantial declines in cancer incidence rates in 2020, likely because of disruptions in screening and diagnostic services. This study aimed to assess the impact of the pandemic on cancer incidence rates in the United States using 2021 incidence data from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results program. The analysis compared observed 2021 cancer incidence rates with expected prepandemic trends, evaluating changes by individual cancer site and stage. Although incidence overall and in many cancer sites the rates were close to prepandemic levels, they did not exhibit a recovery that incorporated the delayed diagnoses from 2020. There were exceptions, however, such as metastatic breast cancer, which showed significantly higher observed rates than expected (rate ratio = 1.09, 95% confidence interval = 1.04 to 1.13). Ongoing monitoring and targeted interventions are needed to address the long-term consequences of the COVID-19 pandemic on cancer care and outcomes.
Published by Oxford University Press 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Schafer EJ, Islami F, Han X, et al.Changes in cancer incidence rates by stage during the COVID-19 pandemic in the US. Int J Cancer. 2024;154(5):786-792. - PubMed
-
- Han X, Yang NN, Nogueira L, et al.Changes in cancer diagnoses and stage distribution during the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic in the USA: a cross-sectional nationwide assessment. Lancet Oncol. 2023;24(8):855-867. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

