A framework for translating tauopathy therapeutics: Drug discovery to clinical trials
- PMID: 39316411
- PMCID: PMC11567863
- DOI: 10.1002/alz.14250
A framework for translating tauopathy therapeutics: Drug discovery to clinical trials
Abstract
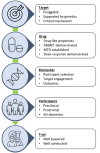
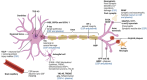
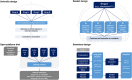
The tauopathies are defined by pathological tau protein aggregates within a spectrum of clinically heterogeneous neurodegenerative diseases. The primary tauopathies meet the definition of rare diseases in the United States. There is no approved treatment for primary tauopathies. In this context, designing the most efficient development programs to translate promising targets and treatments from preclinical studies to early-phase clinical trials is vital. In September 2022, the Rainwater Charitable Foundation convened an international expert workshop focused on the translation of tauopathy therapeutics through early-phase trials. Our report on the workshop recommends a framework for principled drug development and a companion lexicon to facilitate communication focusing on reproducibility and achieving common elements. Topics include the selection of targets, drugs, biomarkers, participants, and study designs. The maturation of pharmacodynamic biomarkers to demonstrate target engagement and surrogate disease biomarkers is a crucial unmet need. HIGHLIGHTS: Experts provided a framework to translate therapeutics (discovery to clinical trials). Experts focused on the "5 Rights" (target, drug, biomarker, participants, trial). Current research on frontotemporal degeneration, progressive supranuclear palsy, and corticobasal syndrome therapeutics includes 32 trials (37% on biologics) Tau therapeutics are being tested in Alzheimer's disease; primary tauopathies have a large unmet need.
Keywords: biomarkers; development; early‐phase clinical trials; preclinical; tauopathy; therapeutics.
© 2024 The Author(s). Alzheimer's & Dementia published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
Steven E. Arnold declares lecture honoraria from: Abbvie, Biogen, and Eisai; serving on advisory boards for: Allyx Therapeutics, Bob's Last Marathon, Cassava, Cortexyme, Sage Therapeutics, and vTv Therapeutics; consulting for: Athira, Boyle‐Shaugnessy Law, Cognito Therapeutics, M3 Biotech, Orthogonal Neuroscience, and Risen Pharmaceutical Technology; and institutional research grant support from: Abbvie, Alzheimer's Association, Alzheimer's Drug Discovery Foundation, Amylyx, Athira, Chromadex, Cyclerion Therapeutics, EIP Pharma, Janssen/Johnson & Johnson, NIH, Novartis, Seer Biosciences, and vTv Therapeutics. Clive Ballard declares grants from Synexus, reMYND, and Novo Nordisk; consultancy fees from Tau Therapeutics, Acadia Pharmaceuticals, Johnson & Johnson, Suven Life Sciences, Sunovion, Exciva, Roche, AbbVie, Orion Pharma, BioExcel, AARP, and Lilly; and honoraria from Bristol Myers Squibb, Axome Therapeutics, Tau Therapeutics, and Biogen. Dirk Beher is a co‐founder, employee, and shareholder of Asceneuron SA. Bradley F. Boeve received honorarium for SAB activities for the Tau Consortium; institutional research grant support from: Alector, Biogen, Transposon, Cognition Therapeutics, EIP Pharma, GE Healthcare; institutional NIH grant support from: P30 AG062677, U19 AG063911, R01 AG038791, U01 NS100620, U19 AG071754, U24 AG056270; institutional foundation support from: Lewy Body Dementia Association, American Brain Foundation; and institutional philanthropic support from: Mayo Clinic Dorothy and Harry T. Mangurian Jr. Lewy Body Dementia Program, the Little Family Foundation, Ted Turner Family Foundation. Adam L. Boxer received grant support from NIH U19AG063911, R01AG073482, R56AG075744, R01AG038791, RF1AG077557, R01AG071756, U01AG045390, Rainwater Charitable Foundation, Bluefield Project to Cure FTD, GHR Foundation, Alzheimer's Association, Association for Frontotemporal Degeneration, Alzheimer's Drug Discovery Foundation, UCSF Parkinson's Spectrum Disorders Center, University of California Cures AD Program; industry research support from: Biogen, Eisai, Regeneron; and did industry consulting for: AGTC, Alchemab, Alector, Amylyx, Arkuda, Arvinas, Arrowhead, Eli Lilly, Merck, Muna, Oscotec, Roche, Switch, Transposon, Wave. Jeffrey L. Cummings reports consulting for: Acadia, Alkahest, AlphaCognition, AriBio, Biogen, Cassava, Cerecin, Cortexyme, Diadem, EIP Pharma, Eisai, GemVax, Genentech, Green Valley, GAP Innovations, Grifols, Janssen, Karuna, Lilly, Lundbeck, LSP, Merck, NervGen, Novo Nordisk, Oligomerix, Ono, Otsuka, PRODEO, Prothena, ReMYND, Resverlogix, Roche, Sage Therapeutics, SignantHealth, Suven, TrueBinding, and Vaxxinity pharmaceutical, assessment, and investment companies; and grant funding from: NIGMS grant P20GM109025, NINDS grant U01NS093334, NIA grant R01AG053798, NIA grant P20AG068053, NIA grant P30AG072959, NIA grant R35AG71476, Alzheimer's Disease Drug Discovery Foundation (ADDF), Ted and Maria Quirk Endowment, and the Joy Chambers‐Grundy Endowment. Penny A. Dacks is an employee of AFTD. Kristophe Diaz is an employee of CurePSP. Colin Ewen is an employee of UCB Pharma. Howard H. Feldman reports UCSD service agreements for consulting from: Axon Neuroscience, Samus Therapeutics, SAB of the Tau Consortium (a program of the Rainwater Charitable Foundation), Novo Nordisk, Genentech (DSMB), Roche/Banner Institute (DMC), and Janssen LLC (DSMB); ADCS clinical trials grant funding from: Annovis (Posiphen), Biohaven (Troriluzole), Vivoryon (Varoglutamstat), AC Immune (ACI‐24‐1301), LuMind (LIFE‐DSR); research funding from: NIA/NIH (U19 AG010483, P30 AG062429, R01 AG061146‐01, 1R56 AG069130‐01, R01 AG051618, 1R01AG070353‐01), CIHR (CAN‐163902), Alzheimer's Association (SG‐20‐690388‐PEACE AD), UC Cures (BRD‐16‐501530), Brain Canada (4469); patent royalties from: Detecting and Treating Dementia (PGRN) Serial Number 12/3‐2691 U.S. Patent No. PCT/US2007/07008. Washington, DC: U.S. Patent and Trademark Office; and funding support from: The USC UCSD Epstein Family Alzheimer Research Collaboration. Brian Fiske works for The Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson's Research and has no conflicts of interest to disclose. M. Isabel Gonzalez has no conflicts of interest to disclose. Glenn A. Harris works for the Rainwater Charitable Foundation, a sponsor of the workshop. Beth J. Hoffman is a full‐time employee of Origami Therapeutics, Inc.; receives grant support from: SBIR Phase I Award No. NINDS R43NS127716; is affiliated with: Huntington's Disease Society of America Board of Trustees; and receives honoraria from: Rainwater Charitable Foundation Tau Consortium, Biofrontera (NASDAQ: BFRI) Board of Directors. Doo Yeon Kim receives grant support from: NIH 1R01AG071496‐01, R01AG062547‐01, 1R01AG057635‐01A1, 1R01AG061891‐01A1, 1R01AG062547‐01, Cure Alzheimer's Fund, Coins for Alzheimer's Research Trust; is a co‐inventor of 3D Alzheimer's in‐a‐dish model; the technology and cell lines are licensed by Millipore/Sigma; and received patent loyalty from Acta Pharmaceutical for the drug candidates detected in cellular model screening. David S. Knopman serves on a data safety monitoring board for the Dominantly Inherited Alzheimer Network Treatment Unit study; was an investigator in Alzheimer's disease clinical trials sponsored by Biogen, Lilly Pharmaceuticals, and the University of Southern California, both of which have ended, and is currently an investigator in a trial in frontotemporal degeneration with Alector; has served as a consultant for Roche, AriBio, Linus Health, Biovie, and Alzeca Biosciences but receives no personal compensation; and receives funding from the NIH. Terina N. Martinez is an employee of the Critical Path Institute and has no conflicts of interest to disclose. Patrick C. May received honoraria for SAB activities for the Tau Consortium (a program of the Rainwater Charitable Foundation) and Cure Alzheimer's Fund. Eric McDade received research funding from: NIA (K23AG046363; U01AG059798), Anonymous Foundation, and GHR; institutional support from: DIAN‐TU Pharma Consortium, Eli Lilly, and Hoffmann La‐Roche; did speaker engagements for: Eli Lilly and Esai; served on an advisory board and DSMB for: Alector, Alzamend, Hoffmann La‐Roche, Merck, and Eli Lilly and is a co‐inventor of the “Methods of diagnosing AD with phosphorylation changes” technology licensed by Washington University to C2N Diagnostics (Washington University holds 5% equity in C2N; Through these relationships, Washington University and Dr. McDade are entitled to receive royalties from the license agreement with C2N). Laura K. Nisenbaum is an employee of the Alzheimer's Drug Discovery Foundation. Jose‐Alberto Palma is an employee of Novartis. Melanie Quintana is an employee of Berry Consultants. Gil D. Rabinovici received grant support from: NIH/NIA P30 AG062422, R35 AG072362, U01 AG057195, R56‐AG075744, U01‐AG082350, Alzheimer's Association, American College of Radiology (contributions from Eli Lilly, GE Healthcare, Life Molecular Imaging), Rainwater Charitable Foundation, Genentech; is a paid consultant for Alector, Eli Lilly, Merck; served on a DSMB for Johnson & Johnson; and is an associate editor for
Figures
References
-
- Goedert M, Wischik CM, Crowther RA, Walker JE, Klug A. Cloning and sequencing of the cDNA encoding a core protein of the paired helical filament of Alzheimer disease: identification as the microtubule‐associated protein tau. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988;85(11):4051‐4055. doi:10.1073/pnas.85.11.4051 - DOI - PMC - PubMed

