Proteogenomic analysis integrated with electronic health records data reveals disease-associated variants in Black Americans
- PMID: 39316441
- PMCID: PMC11527441
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI181802
Proteogenomic analysis integrated with electronic health records data reveals disease-associated variants in Black Americans
Abstract
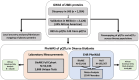
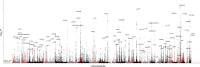
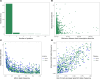
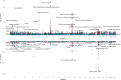
BACKGROUNDMost GWAS of plasma proteomics have focused on White individuals of European ancestry, limiting biological insight from other ancestry-enriched protein quantitative loci (pQTL).METHODSWe conducted a discovery GWAS of approximately 3,000 plasma proteins measured by the antibody-based Olink platform in 1,054 Black adults from the Jackson Heart Study (JHS) and validated our findings in the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA). The genetic architecture of identified pQTLs was further explored through fine mapping and admixture association analysis. Finally, using our pQTL findings, we performed a phenome-wide association study (PheWAS) across 2 large multiethnic electronic health record (EHR) systems in All of Us and BioMe.RESULTSWe identified 1,002 pQTLs for 925 protein assays. Fine mapping and admixture analyses suggested allelic heterogeneity of the plasma proteome across diverse populations. We identified associations for variants enriched in African ancestry, many in diseases that lack precise biomarkers, including cis-pQTLs for cathepsin L (CTSL) and Siglec-9, which were linked with sarcoidosis and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, respectively. We found concordant associations across clinical diagnoses and laboratory measurements, elucidating disease pathways, including a cis-pQTL associated with circulating CD58, WBC count, and multiple sclerosis.CONCLUSIONSOur findings emphasize the value of leveraging diverse populations to enhance biological insights from proteomics GWAS, and we have made this resource readily available as an interactive web portal.FUNDINGNIH K08 HL161445-01A1; 5T32HL160522-03; HHSN268201600034I; HL133870.
Keywords: Genetic diseases; Genetics; Immunology; Population genetics; Proteomics.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HHSN268201100037C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HG003067/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL120393/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095167/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201800012I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201800015I/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000040/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- K23 DK127073/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095160/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00002/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201500003C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095161/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00005/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES010126/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201800012C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095168/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL120393/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001079/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095169/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201800014I/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 HL161445/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00001/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201800014C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095159/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00003/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM135123/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL105756/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201800001C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201800013I/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001420/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00004/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00007/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095163/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201800011C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K23 HL164980/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL133870/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201500003I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095166/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K23 HL150327/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201800010I/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00006/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL117626/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095162/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001881/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201800011I/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095165/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095164/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

