Extracellular vesicle transfer of miR-1 to adipose tissue modifies lipolytic pathways following resistance exercise
- PMID: 39316445
- PMCID: PMC11601556
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.182589
Extracellular vesicle transfer of miR-1 to adipose tissue modifies lipolytic pathways following resistance exercise
Abstract
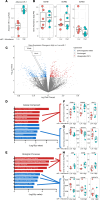
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) have emerged as important mediators of intertissue signaling and exercise adaptations. In this human study, we provide evidence that muscle-specific microRNA-1 (miR-1) was transferred to adipose tissue via EVs following an acute bout of resistance exercise. Using a multimodel machine learning automation tool, we discovered muscle primary miR-1 transcript and CD63+ EV count in circulation as top explanatory features for changes in adipose miR-1 levels in response to resistance exercise. RNA-Seq and in-silico prediction of miR-1 target genes identified caveolin 2 (CAV2) and tripartite motif containing 6 (TRIM6) as miR-1 target genes downregulated in the adipose tissue of a subset of participants with the highest increases in miR-1 levels following resistance exercise. Overexpression of miR-1 in differentiated human adipocyte-derived stem cells downregulated these miR-1 targets and enhanced catecholamine-induced lipolysis. These data identify a potential EV-mediated mechanism by which skeletal muscle communicates with adipose tissue and modulates lipolysis via miR-1.
Keywords: Adipose tissue; Metabolism; Muscle biology; Skeletal muscle; Transport.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

