Tuning Nanographene-Enhanced Raman Scattering for Rapid Label-Free Detection of Amino Acids
- PMID: 39316462
- PMCID: PMC11472263
- DOI: 10.1021/acsami.4c08298
Tuning Nanographene-Enhanced Raman Scattering for Rapid Label-Free Detection of Amino Acids
Abstract
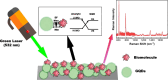
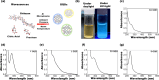
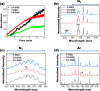
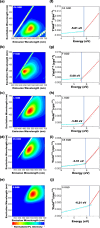
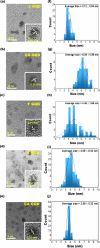
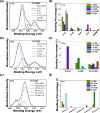
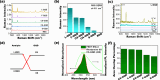
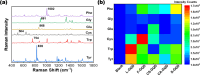
The rapid and sensitive detection of amino acids is important not only for fundamental studies but also for the establishment of a healthy society. However, conventional detection methods have been hampered by the difficulties of low sensitivity, long sampling and detection times, and expensive operation and instruments. Here, we report the plasma engineering of bioresource-derived graphene quantum dots (GQDs) as surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS)-active materials for the rapid and sensitive detection of amino acids. Surface-functionalized GQDs with tuned structures and band gaps were synthesized from earth-abundant bioresources by using reactive microplasmas under ambient conditions. Detailed microscopy and spectroscopy studies indicate that the SERS properties of the synthesized GQDs can be tuned by controlling the band gaps of synthesized GQDs. The plasma-synthesized metal-free GQDs with surface functionalities showed improved SERS properties for rapid amino acid detection with low detection limits of 10-5 M for tyrosine and phenylalanine. Theoretical calculations suggest that charge transfer between GQDs and amino acids can enhance the SERS response of the GQDs. Our work provides insights into the controlled engineering of SERS-active nanographene-based materials using the plasma-enhanced method.
Keywords: Raman scattering; amino acids; band gap tuning; biosensors; graphene quantum dots; plasmas.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Recent Advances in Inflammatory Diagnosis with Graphene Quantum Dots Enhanced SERS Detection.Biosensors (Basel). 2022 Jun 27;12(7):461. doi: 10.3390/bios12070461. Biosensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35884264 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Europium-decorated graphene quantum dots as a fluorescent probe for label-free, rapid and sensitive detection of Cu(2+) and L-cysteine.Anal Chim Acta. 2015 Sep 3;891:261-8. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2015.08.011. Epub 2015 Aug 22. Anal Chim Acta. 2015. PMID: 26388385
-
Utilization of doped GQDs for ultrasensitive detection of catastrophic melamine: A new SERS platform.Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2020 Jan 5;224:117352. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2019.117352. Epub 2019 Jul 8. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2020. PMID: 31344580
-
Plasma Nanoengineering of Bioresource-Derived Graphene Quantum Dots as Ultrasensitive Environmental Nanoprobes.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022 Nov 23;14(46):52289-52300. doi: 10.1021/acsami.2c15251. Epub 2022 Nov 8. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022. PMID: 36349361
-
Gold-based hybrid nanomaterials for biosensing and molecular diagnostic applications.Biosens Bioelectron. 2016 Jun 15;80:543-559. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2016.02.015. Epub 2016 Feb 8. Biosens Bioelectron. 2016. PMID: 26894985 Review.
Cited by
-
Optimized Sensitivity in Copper(II) Ion Detection: Sustainable Fabrication of Fluorescence Red-Shifted Graphene Quantum Dots via Electron-Withdrawing Modulation.Molecules. 2025 Mar 10;30(6):1244. doi: 10.3390/molecules30061244. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40142020 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Parker M. F. L.; Luu J. M.; Schulte B.; Huynh T. L.; Stewart M. N.; Sriram R.; Yu M. A.; Jivan S.; Turnbaugh P. J.; Flavell R. R.; Rosenberg O. S.; Ohliger M. A.; Wilson D. M. Sensing Living Bacteria in Vivo Using d-Alanine-Derived 11C Radiotracers. ACS Cent. Sci. 2020, 6 (2), 155–165. 10.1021/acscentsci.9b00743. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhu D.; Bai Z.; Ma H.; Tan L.; Pang H.; Wang X. High performance simultaneous detection of β-nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide and l-tryptophan in human serum based on a novel nanocomposite of ferroferric oxide-functionalized polyoxometalates. Sens. Actuators, B 2020, 309, 12778710.1016/j.snb.2020.127787. - DOI
-
- Tuccitto N.; Fichera L.; Ruffino R.; Cantaro V.; Sfuncia G.; Nicotra G.; Sfrazzetto G. T.; Li-Destri G.; Valenti A.; Licciardello A.; Torrisi A. Carbon Quantum Dots as Fluorescence Nanochemosensors for Selective Detection of Amino Acids. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4 (6), 6250–6256. 10.1021/acsanm.1c01046. - DOI
-
- Bahadoran A.; Jabarabadi M. K.; Mahmood Z. H.; Bokov D.; Janani B. J.; Fakhri A. Quick and sensitive colorimetric detection of amino acid with functionalized-silver/copper nanoparticles in the presence of cross linker, and bacteria detection by using DNA-template nanoparticles as peroxidase activity. Spectrochim. Acta, Part A 2022, 268, 12063610.1016/j.saa.2021.120636. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

