Causal associations of air pollution with rheumatoid arthritis: A transethnic Mendelian randomization study
- PMID: 39316602
- PMCID: PMC11421788
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0307514
Causal associations of air pollution with rheumatoid arthritis: A transethnic Mendelian randomization study
Abstract
Background: Rheumatoid arthritis is a common rheumatic disease, and its onset is closely related to genetic and environmental factors, however, the relationship between air pollution and RA is still hotly debated. Further investigation of the relationship between air pollution and rheumatoid arthritis is conducive to a comprehensive understanding of the risk factors of the disease, providing certain value for the clinical prevention and treatment of RA.
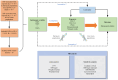
Methods: We used a Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization approach, integrating the large-scale public genomewide association study, to assess the genetically predicted causal effect of air pollution (including: PM2.5, PM2.5-10, PM10, nitrogen dioxide, nitrogen oxides) on RA in European and European East Asian populations, respectively. Indicators related to air pollution (2,505 individuals to 423,796 individuals), including European and East Asian populations were obtained from the Integrative Epidemiology Unit open GWAS project. Published East Asian RA data were also obtained from the IEU open GWAS project (212,453 individuals), while large-scale publicly available European RA data were obtained from finngen R10 (13,621 cases and 262,844 controls). Inverse variance weighting was used as the primary analytical method, complemented by MR-egger, Weighed median, and Weighted mode results. Cochran Q tested for heterogeneity, and MR-Egger regression analyses were performed to test for multiplicity. leave-one-out analysis allowed for the robustness and reliability were assessed.
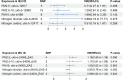
Results: No statistically significant effects of PM2.5, PM2.5-10, PM10, nitrogen dioxide, nitrogen oxides and RA were observed in either European or East Asian populations. Results from European data: PM2.5 (IVW OR: 0.71; 95% CI: 0.27-1.91; p = 0.498; number of SNPs: 5), PM2.5-10 (IVW OR: 1.20; 95% CI: 0.61-2.40; p = 0.596; number of SNPs: 15), PM10 (IVW OR: 1.69; 95% CI: 0.84-3.39; p = 0.142; number of SNPs: 9), nitrogen dioxide (IVW OR: 3.88; 95% CI: 0.19-77.77; p = 0.375; number of SNPs: 2), nitrogen oxides (IVW OR: 0.51; 95% CI: 0.16-1.67; p = 0.268; number of SNPs: 4). East Asian data results: PM2.5 (IVW OR: 1.16; 95% CI: 0.98-1.38; p = 0.086; number of SNPs: 4), PM2.5-10 (IVW OR: 1.14; 95% CI: 0.95-1.38; p = 0.166; number of SNPs: 2), PM10 (IVW OR: 0.95; 95% CI: 0.81-1.11; p = 0.503; number of SNPs: 3), nitrogen dioxide (IVW OR: 0.87; 95% CI: 0.76-1.00; p = 0.051; number of SNPs: 6), nitrogen oxides (IVW OR: 0.96; 95% CI: 0.82-1.14; p = 0.671; number of SNPs: 3). No signs of pleiotropy or heterogeneity were observed in the MR-Egger intercept, MR-PRESSO and Cochrane's Q (p>0.05). In addition, no outliers were found in the MR-PRESSO analysis. The results were further validated by leave-one-out tests, confirming the robustness of the findings.
Conclusions: We performed transethnic MR analysis suggesting that there may not be a genetically predicted causal relationship between air pollution and RA.
Copyright: © 2024 He et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association between air pollution and primary liver cancer in European and east Asian populations: a Mendelian randomization study.Front Public Health. 2023 Jul 27;11:1212301. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1212301. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37575092 Free PMC article.
-
Causal relationship between air pollution and infections: a two-sample Mendelian randomization study.Front Public Health. 2024 Aug 1;12:1409640. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1409640. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39148655 Free PMC article.
-
Cross ethnic Mendelian randomization analysis reveals causal relationship between air pollution and risk of kidney stones.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 9;15(1):12132. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-97436-y. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40204920 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic insights into the causal relationship between air pollutants and atrial fibrillation: a Mendelian randomization study.Int J Environ Health Res. 2025 May 16:1-11. doi: 10.1080/09603123.2025.2502635. Online ahead of print. Int J Environ Health Res. 2025. PMID: 40376711 Review.
-
Analysis of the causal relationship between immune cells and rheumatoid arthritis from the perspective of genetic variation: a bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization study.Adv Rheumatol. 2024 Nov 1;64(1):83. doi: 10.1186/s42358-024-00425-4. Adv Rheumatol. 2024. PMID: 39487558 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

