Inflammation indices in association with periodontitis and cancer
- PMID: 39317462
- PMCID: PMC11579835
- DOI: 10.1111/prd.12612
Inflammation indices in association with periodontitis and cancer
Abstract
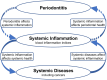
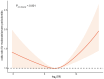
Inflammation is a complex physiological process that plays a pivotal role in many if not all pathological conditions, including infectious as well as inflammatory diseases, like periodontitis and autoimmune disorders. Inflammatory response to periodontal biofilms and tissue destruction in periodontitis is associated with the release of inflammatory mediators. Chronic inflammation can promote the development of cancer. Persistence of inflammatory mediators plays a crucial role in this process. Quantification and monitoring of the severity of inflammation in relation to cancer is essential. Periodontitis is mainly quantified based on the severity and extent of attachment loss and/or pocket probing depth, in addition with bleeding on probing. In recent years, studies started to investigate inflammation indices in association with periodontal diseases. To date, only few reviews have been published focusing on the relationship between blood cell count, inflammation indices, and periodontitis. This review presents a comprehensive overview of different systemic inflammation indices, their methods of measurement, and the clinical applications in relation to periodontitis and cancer. This review outlines the physiological basis of inflammation and the underlying cellular and molecular mechanisms of the parameters described. Key inflammation indices are commonly utilized in periodontology such as the neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio. Inflammation indices like the platelet to lymphocyte ratio, platelet distribution width, plateletcrit, red blood cell distribution width, lymphocyte to monocyte ratio, delta neutrophil index, and the systemic immune inflammation index are also used in hospital settings and will be discussed. The clinical roles and limitations, relationship to systemic diseases as well as their association to periodontitis and treatment response are described.
Keywords: cancer; delta neutrophil index; inflammation indices; inflammation markers; lymphocyte to monocyte ratio; neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio; periodontitis; platelet distribution width; platelet to lymphocyte ratio; plateletcrit; red blood cell distribution width; systemic immune inflammation index.
© 2024 The Author(s). Periodontology 2000 published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have stated explicitly that there are no conflicts of interest in connection with this article.
Figures

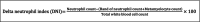





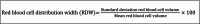
References
-
- Tonetti MS, Greenwell H, Kornman KS. Staging and grading of periodontitis: framework and proposal of a new classification and case definition. J Clin Periodontol. 2018;45(Suppl 20):S149‐S161. - PubMed
-
- Meyle J, Chapple I. Molecular aspects of the pathogenesis of periodontitis. Periodontol 2000. 2015;69(1):7‐17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

