Investigation of the knowledge, attitude and practice regarding nutrition in older adults with tuberculosis and diabetes: a cross-sectional study in Eastern China
- PMID: 39317504
- PMCID: PMC11423730
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-087325
Investigation of the knowledge, attitude and practice regarding nutrition in older adults with tuberculosis and diabetes: a cross-sectional study in Eastern China
Abstract
Objectives: Older adults with tuberculosis and diabetes have special needs regarding dietary nutrition. This study aimed to investigate the knowledge, attitude and practice (KAP) regarding dietary nutrition among older adults with those two conditions.
Design: Cross-sectional study.
Setting: Three tertiary medical centres in China.
Participants: Adults over 60 year old diagnosed with tuberculosis and diabetes.
Interventions: Between July 2023 and October 2023.
Primary and secondary outcome measures: Demographic characteristics and KAP scores collected by self-designed questionnaire.
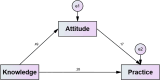
Results: A total of 456 valid questionnaires were analysed, with 261 (57.24%) participants being over 70 years old. The mean scores were 6.84±3.16 (possible range: 0-24) for knowledge, 23.23±2.23 (possible range: 8-40) for attitude and 22.73±3.14 (possible range: 8-40) for practice, respectively. Correlation analysis revealed significant positive correlations between knowledge and attitude (r=0.287, p<0.001), knowledge and practice (r=0.189, p<0.001) and attitude and practice (r=0.176, p<0.001). Structural equation modelling demonstrated that knowledge significantly influenced attitude (β=0.343, 95% CI (0.257 to 0.422), p<0.001) and practice (β=0.245, 95% CI (0.101 to 0.405), p<0.001) and attitude significantly influenced practice (β=0.274, 95% CI (0.146 to 0.405), p<0.001).
Conclusions: The study highlights a need for improvements in dietary nutrition practices for older adults with tuberculosis and diabetes. Findings emphasise the urgency of enhancing dietary education among this population in China. Implementation of targeted educational programmes is warranted to improve knowledge, foster positive attitudes and encourage healthier dietary practices, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes and well-being.
Keywords: diabetes & endocrinology; education, medical; geriatric medicine; health education; tuberculosis.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Similar articles
-
Knowledge, attitudes and practices of healthcare professionals in the management of patients with hypertension and concurrent bronchial asthma: a cross-sectional study in the Yellow River Delta region of China.BMJ Open. 2025 Jan 21;15(1):e088743. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-088743. BMJ Open. 2025. PMID: 39842923 Free PMC article.
-
Knowledge, attitudes, and practices toward postoperative rehabilitation among females with rotator cuff injury: a cross-sectional study.J Orthop Surg Res. 2025 May 26;20(1):516. doi: 10.1186/s13018-025-05928-4. J Orthop Surg Res. 2025. PMID: 40420194 Free PMC article.
-
Empowering Nursing Practices: Enhancing Patient Care Through Knowledge, Attitude and Practice Towards Urinary Catheterisation in Taicang City.Nurs Open. 2024 Dec;11(12):e70111. doi: 10.1002/nop2.70111. Nurs Open. 2024. PMID: 39639465 Free PMC article.
-
Knowledge, attitudes and practices regarding pulmonary rehabilitation among patients with chronic respiratory diseases: a cross-sectional questionnaire-based study in a tertiary hospital in China.BMJ Open. 2025 Jan 21;15(1):e085944. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-085944. BMJ Open. 2025. PMID: 39842929 Free PMC article.
-
Nutrition and Exercise Knowledge, Attitude, and Practice: A Scoping Review of Assessment Questionnaires in Cancer Survivorship.Nutrients. 2025 Apr 23;17(9):1412. doi: 10.3390/nu17091412. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40362721 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical