Statistically and functionally fine-mapped blood eQTLs and pQTLs from 1,405 humans reveal distinct regulation patterns and disease relevance
- PMID: 39317738
- PMCID: PMC11525184
- DOI: 10.1038/s41588-024-01896-3
Statistically and functionally fine-mapped blood eQTLs and pQTLs from 1,405 humans reveal distinct regulation patterns and disease relevance
Erratum in
-
Publisher Correction: Statistically and functionally fine-mapped blood eQTLs and pQTLs from 1,405 humans reveal distinct regulation patterns and disease relevance.Nat Genet. 2024 Oct;56(10):2281. doi: 10.1038/s41588-024-01959-5. Nat Genet. 2024. PMID: 39333769 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
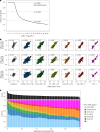
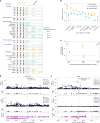
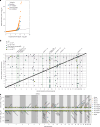
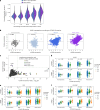
Studying the genetic regulation of protein expression (through protein quantitative trait loci (pQTLs)) offers a deeper understanding of regulatory variants uncharacterized by mRNA expression regulation (expression QTLs (eQTLs)) studies. Here we report cis-eQTL and cis-pQTL statistical fine-mapping from 1,405 genotyped samples with blood mRNA and 2,932 plasma samples of protein expression, as part of the Japan COVID-19 Task Force (JCTF). Fine-mapped eQTLs (n = 3,464) were enriched for 932 variants validated with a massively parallel reporter assay. Fine-mapped pQTLs (n = 582) were enriched for missense variations on structured and extracellular domains, although the possibility of epitope-binding artifacts remains. Trans-eQTL and trans-pQTL analysis highlighted associations of class I HLA allele variation with KIR genes. We contrast the multi-tissue origin of plasma protein with blood mRNA, contributing to the limited colocalization level, distinct regulatory mechanisms and trait relevance of eQTLs and pQTLs. We report a negative correlation between ABO mRNA and protein expression because of linkage disequilibrium between distinct nearby eQTLs and pQTLs.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Q.S.W. is an employee of Calico Life Sciences. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

