Exercise activates AMPK in mouse and human pancreatic islets to decrease senescence
- PMID: 39317751
- PMCID: PMC12005094
- DOI: 10.1038/s42255-024-01130-8
Exercise activates AMPK in mouse and human pancreatic islets to decrease senescence
Abstract
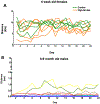
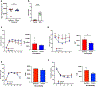
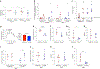
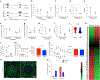
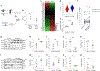
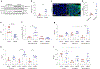
Beta (β)-cell senescence contributes to type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). While exercise is vital for T2DM management and significantly affects cellular ageing markers, its effect on β-cell senescence remains unexplored. Here, we show that short-term endurance exercise training (treadmill running, 1 h per day for 10 days) in two male and female mouse models of insulin resistance decreases β-cell senescence. In vivo and in vitro experiments revealed that this effect is mediated, at least in part, by training-induced increases in serum glucagon, leading to activation of 5'-AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) signalling in β-cells. AMPK activation resulted in the nuclear translocation of NRF2 and decreased expression of senescence markers and effectors. Remarkably, human islets from male and female donors with T2DM treated with serum collected after a 10-week endurance exercise training programme showed a significant decrease in the levels of senescence markers. These findings indicate that exercise training decreases senescence in pancreatic islets, offering promising therapeutic implications for T2DM.
© 2024. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Figures

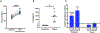
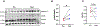



References
-
- Dunning T, Sinclair A & Colagiuri S New IDF Guideline for managing type 2 diabetes in older people. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract 103, 538–540 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Salomon JA et al. Healthy life expectancy for 187 countries, 1990–2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden Disease Study 2010. Lancet 380, 2144–2162 (2012). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

