Analysis of genomic alternations in epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-T790M-mutated non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients with acquired resistance to osimertinib therapy
- PMID: 39317868
- PMCID: PMC12033095
- DOI: 10.1007/s12094-024-03727-7
Analysis of genomic alternations in epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-T790M-mutated non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients with acquired resistance to osimertinib therapy
Abstract
Background and objectives: Genomic alterations after resistance to osimertinib therapy in advanced T790M-mutated non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) are complex and poorly understood. In this study, we aimed to detect these genomic alternations via comprehensive next-generation sequencing (NGS) of tissue and liquid biopsies.
Patients and methods: From September 2020 to June 2021, 31 stage IIIB/IV T790M-mutated NSCLC patients who exhibited progressive disease after osimertinib therapy and provided written informed consent were recruited. Liquid and tissue biopsy samples for NGS testing were collected from 31 and 18 patients, respectively. Eighteen study patients had paired NGS data from tissue and liquid biopsies.
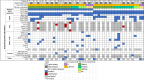
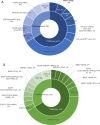
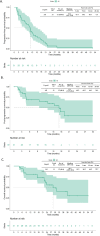
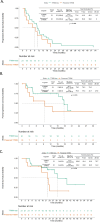
Results: With respect to the T790M mutation status, the preservation and loss rates were 33% and 67%, respectively, in both liquid and tissue biopsy samples. Five patients (16.1%) had the C797S mutation (4 liquid samples and 1 tissue sample). Two (6.5%) had MET mutations, 3 (9.7%) had BRAF-V600E mutations, and 1 (3.2%) had a KRAS-G12C mutation. Among the 18 patients who underwent tissue rebiopsies, those with preserved T790M mutation had significantly longer progression-free survival (PFS) with osimertinib therapy than those with T790M mutation loss (10.8 vs. 5.0 months, P = 0.045). Among all patients, those with T790M mutation loss in liquid biopsy samples had longer PFS after osimertinib therapy (10.8 vs. 7.5 months, P = 0.209) and postprogression survival (17.7 vs. 9.6 months, P = 0.132) than those with preserved T790M mutation based on liquid biopsies.
Conclusions: NGS using either tissue or liquid biopsy samples from advanced T790M-mutated NSCLC patients with acquired resistance to osimertinib therapy can detect various genomic alternations. Future studies focusing on subsequent tailored therapies on the basis of NGS results are warranted.
Keywords: Acquired resistance; Epidermal growth factor receptor mutation; Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC); Osimertinib; T790M; Tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: All the authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Osimertinib for EGFR-Mutant NSCLC Patients With Acquired T790M and EGFR Amplification After First-Generation EGFR-TKI Resistance.Cancer Sci. 2025 Mar;116(3):753-763. doi: 10.1111/cas.16437. Epub 2024 Dec 31. Cancer Sci. 2025. PMID: 39741120 Free PMC article.
-
Audit of Molecular Mechanisms of Primary and Secondary Resistance to Various Generations of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Known Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Mutant Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Patients in a Tertiary Centre.Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2022 Nov;34(11):e451-e462. doi: 10.1016/j.clon.2022.06.003. Epub 2022 Jul 7. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2022. PMID: 35810049
-
Exploring the resistance mechanisms of second-line osimertinib and their prognostic implications using next-generation sequencing in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer.Eur J Cancer. 2021 May;148:202-210. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2021.01.052. Epub 2021 Mar 18. Eur J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33744716
-
Complete response in a lung adenocarcinoma with pleural metastases initially treated with gefitinib and switched to osimertinib after cerebral oligo-progression with unknown T790M mutation: a case report and review of literature.J Med Case Rep. 2024 Aug 8;18(1):374. doi: 10.1186/s13256-024-04706-w. J Med Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 39113087 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy and safety of osimertinib in treating EGFR-mutated advanced NSCLC: A meta-analysis.Int J Cancer. 2019 Jul 1;145(1):284-294. doi: 10.1002/ijc.32097. Epub 2019 Jan 20. Int J Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30613959 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Clinical outcome analysis of different first‑ and second‑generation EGFR‑tyrosine kinase inhibitors in untreated patients with EGFR‑mutated non‑small cell lung cancer with baseline brain metastasis.Oncol Lett. 2025 Feb 26;29(4):201. doi: 10.3892/ol.2025.14947. eCollection 2025 Apr. Oncol Lett. 2025. PMID: 40070793 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sharma SV, Bell DW, Settleman J, Haber DA. Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7:169–81. - PubMed
-
- Zhou H, Geng F, Chen Y, Du J, Zhang X, Liu B, et al. The mineral dust-induced gene, mdig, regulates angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis in lung adenocarcinoma by modulating the expression of VEGF-A/C/D via EGFR and HIF-1α signaling. Oncol Rep. 2021;45(5):60. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 111-2628-B-182A-003/Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan
- 112-2314-B-182 -067/Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan
- 109-2314-B-182-080-MY3/Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan
- 111-2811-B-182-017/Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan
- CMRPG3M0971/Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Linkou
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

