Factors associated with length of stay in medium secure units: A realist review
- PMID: 39318046
- PMCID: PMC11605979
- DOI: 10.1177/10398562241286627
Factors associated with length of stay in medium secure units: A realist review
Abstract
Objectives: This 'Realist Review' aimed to investigate the factors associated with length of stay and outcomes of medium secure care to help inform the development of a local secure care pathway.
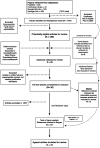
Method: The searches generated a total of 1570 entries across multiple search engines. Following removal of duplicates, application of inclusion/exclusion criteria and selection of articles, a total of 18 were reviewed in detail, including a further five articles obtained from references and the explored grey literature.
Results: Several issues influenced not only admission to medium secure units, but also the outcomes. Many articles were retrospective studies relying on administrative data. The realist synthesis provides contextual data to inform program development.
Conclusions: The existing literature, though variable in quality, was limited by the varied jurisdictions and contexts. However it may be useful to inform care pathways for the optimal use of medium secure beds.
Keywords: forensic; length of stay; medium secure mental health units; realist review.
Conflict of interest statement
DisclosureThe author(s) declared the following potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: The authors declare that research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Volume and health outcomes: evidence from systematic reviews and from evaluation of Italian hospital data].Epidemiol Prev. 2013 Mar-Jun;37(2-3 Suppl 2):1-100. Epidemiol Prev. 2013. PMID: 23851286 Italian.
-
Factors within the clinical encounter that impact upon risk assessment within child and adolescent mental health services: a rapid realist synthesis.Health Soc Care Deliv Res. 2024 Jan;12(1):1-107. doi: 10.3310/VKTY5822. Health Soc Care Deliv Res. 2024. PMID: 38314750
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
-
Consumer-providers of care for adult clients of statutory mental health services.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Mar 28;2013(3):CD004807. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004807.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. PMID: 23543537 Free PMC article.
-
Single induction dose of etomidate versus other induction agents for endotracheal intubation in critically ill patients.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Jan 8;1(1):CD010225. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010225.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 25568981 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brown K, Fahy T. Medium secure units: pathways of care and time to discharge over a four-year period in South London. J Forensic Psychiatr Psychol 2009; 20(2): 268–277.
-
- Simpson AWB, Scott PD, Prins HA. The butler committee’s report. Br J Criminol 1976; 16(2): 175–183, Retrieved from. https://www.jstor.org/stable/23636312 (accessed 6th January 2022).
-
- Robertson P, Barnao M, Ward T. Rehabilitation frameworks in forensic mental health. Aggress Violent Behav 2011; 16(6): 472–484. DOI: 10.1016/j.avb.2011.03.003. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources