Platelet-rich plasma intra-articular knee injections from open preparation techniques do not pose a higher risk of joint infection: A systematic review of 91 randomized controlled trials and 5914 injections
- PMID: 39318712
- PMCID: PMC11420304
- DOI: 10.1002/jeo2.70002
Platelet-rich plasma intra-articular knee injections from open preparation techniques do not pose a higher risk of joint infection: A systematic review of 91 randomized controlled trials and 5914 injections
Abstract
Purpose: To compare the infection rate of intraarticular platelet-rich plasma (PRP) knee injections between open and closed techniques in randomized controlled trials (RCTs) published in the last decade.
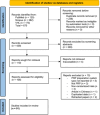
Methods: Following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses guidelines, PubMed, Scopus and Virtual Health Library were accessed in October 2022 using the terms 'platelet-rich plasma', 'PRP', 'knee' and 'tibiofemoral' alone and in combination with Boolean operators AND/OR. RCTs published during the last 10 years evaluating PRP intra-articular knee injections were considered eligible. Studies were excluded if the kit/preparation technique was not described. Data were presented using individual studies' absolute values, totals, and pooled percentages. Publication bias was assessed using the ROBIS tool.
Results: Ninety-one studies met the predetermined eligibility criteria. Forty-one implemented a closed technique, while 50 were open. All studies implementing a closed technique disclosed their commercial kits. Only 16 studies (17.58%) failed to report joint infections. Among the studies reporting joint infections as outcomes, 30 implemented a closed technique with 1195 patients, 1921 intra-articular knee injections and 95.44% of patient follow-up. On the other hand, 45 of them implemented an open technique with 2290 patients, 3993 intra-articular knee injections and 97.07% of patient follow-up. No patient had a joint infection among the included studies. Thirty-three studies prepared their PRP in controlled environments (36.26%). Most studies did not report where the preparation occurred (48.35%). Only twelve studies disclosed using laminar flow during preparation (13.19%). The infection rate for both techniques was 0 per 1000 knee injections.
Conclusion: Open PRP preparation techniques do not pose a higher risk of joint infection and can lower manufacturing costs when appropriate facilities are available. However, PRP preparation setting and laminar flow implementation data are deficient, and minimal requirements for good manufacturing practices demand further studies while adhering to local and regional regulations.
Level of evidence: Level I, systematic review of RCTs.
Keywords: closed technique; good manufacturing practices; joint infection; laminar flow; open technique; orthobiologics; platelet‐rich plasma.
© 2024 The Author(s). Journal of Experimental Orthopaedics published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Society of Sports Traumatology, Knee Surgery and Arthroscopy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Single intra-articular injection with or without intra-osseous injections of platelet-rich plasma in the treatment of osteoarthritis knee: A single-blind, randomized clinical trial.Injury. 2022 Mar;53(3):1247-1253. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2022.01.012. Epub 2022 Jan 7. Injury. 2022. PMID: 35033356 Clinical Trial.
-
The Use of Intra-articular Platelet-Rich Plasma as a Therapeutic Intervention for Hip Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Am J Sports Med. 2023 Jul;51(9):2487-2497. doi: 10.1177/03635465221095563. Epub 2022 Jun 7. Am J Sports Med. 2023. PMID: 35971803 Free PMC article.
-
Intra-articular injections of platelet-rich plasma in symptomatic knee osteoarthritis: a consensus statement from French-speaking experts.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2021 Oct;29(10):3195-3210. doi: 10.1007/s00167-020-06102-5. Epub 2020 Jun 24. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2021. PMID: 32583023 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Intra-articular Injections in Hip Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review of Randomized Clinical Trials.Cureus. 2024 Oct 21;16(10):e72057. doi: 10.7759/cureus.72057. eCollection 2024 Oct. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39569300 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Intra-articular Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Versus Corticosteroid Injections in the Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review of Randomized Clinical Trials.Cureus. 2025 Mar 21;17(3):e80948. doi: 10.7759/cureus.80948. eCollection 2025 Mar. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40260368 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The role of platelet-rich plasma in biomedicine: A comprehensive overview.iScience. 2025 Jan 3;28(2):111705. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.111705. eCollection 2025 Feb 21. iScience. 2025. PMID: 39898035 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Acosta‐Olivo, C. , Esponda‐Colmenares, F. , Vilchez‐Cavazos, F. , Lara‐Arias, J. , Mendoza‐Lemus, O. & Ramos‐Morales, T. (2014) Plasma rico en plaquetas versus paracetamol oral para el tratamiento de la osteoartrosis temprana de rodilla. Estudio preliminar [Platelet rich plasma versus oral paracetamol for the treatment of early knee osteoarthritis. Preliminary study]. Cirugia y cirujanos, 82(2), 163–169. - PubMed
-
- Angoorani, H. , Mazaherinezhad, A. , Marjomaki, O. & Younespour, S. (2015) Treatment of knee osteoarthritis with platelet‐rich plasma in comparison with transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation plus exercise: a randomized clinical trial. Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran, 29, 223. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anz, A.W. , Hubbard, R. , Rendos, N.K. , Everts, P.A. , Andrews, J.R. & Hackel, J.G. (2020) Bone marrow aspirate concentrate is equivalent to platelet‐rich plasma for the treatment of knee osteoarthritis at 1 year: a prospective, randomized trial. Orthopaedic Journal of Sports Medicine, 8(2), 2325967119900958. Available from: 10.1177/2325967119900958 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous