Impact of graphene incorporation in dental implants-A scoping review
- PMID: 39318807
- PMCID: PMC11420491
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37751
Impact of graphene incorporation in dental implants-A scoping review
Abstract
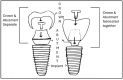
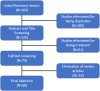
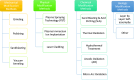
There are numerous variables governing the formation of new bone around a dental implant. Of those variables, the implant surface is an important factor influencing the quality of osseointergration. Numerous techniques and materials have been used to alter the surface of an implant to enhance osseointergration and improve the survival and success rate. One such modification is utilizing graphene to modify the surface of an implant. This paper summarizes data collected form articles published in online databases in the past 10 years about the various means of modifying the implant surfaces and provides an in-depth review of the impact of graphene incorporation in dental implants. The document comprised of different sections and emphasized on the use of graphene as an implant surface coating material. The role of graphene on flexural strength, hardness and corrosion resistance have been discussed under mechanical properties whereas the potential of this combination on the osteogenesis, osseointergration and soft tissue seal is covered under biological properties. Lastly, how this combination acts as a drug delivery carrier and renders antimicrobial property has been addressed under pharmacological properties. This review has highlighted the various applications of graphene in the field of implant dentistry. It has outlined the various implant surface modifying methods and thrown light on the various affect this combination has on the mechanical, biological and pharmacological properties. Considering the various research done on the material, it can be concluded that graphene does have a bright future in implant dentistry and continued research in this area will provide fruitful benefits.
Keywords: Graphene oxide; Implant surface modification; Osseointegration; Reduced graphene oxide; Titanium implants.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Xu A., Alhamad M., Ampadi Ramachandran R., Shukla A., Barão V.A., Sukotjo C., Mathew M.T. Peri-implantitis in relation to titanium corrosion: current Status and future perspectives. J. Bio- Tribo-Corros. 2022;8:46. doi: 10.1007/s40735-022-00644-6. - DOI
-
- Inchingolo A.M., Malcangi G., Inchingolo A.D., Mancini A., Palmieri G., Di Pede C., Piras F., Inchingolo F., Dipalma G., Patano A. Potential of graphene-functionalized titanium surfaces for dental implantology: systematic review. Coatings. 2023;13:725. doi: 10.3390/coatings13040725. - DOI
-
- Zafar M.S., Farooq I., Awais M., Najeeb S., Khurshid Z., Zohaib S. In: Biomed. Ther. Clin. Appl. Bioact. Glas. Kaur G., editor. Woodhead Publishing; 2019. Chapter 11 - bioactive surface coatings for enhancing osseointegration of dental implants; pp. 313–329. - DOI
-
- Rokaya D., Srimaneepong V., Qin J., Siraleartmukul K., Siriwongrungson V. Graphene oxide/silver nanoparticle coating produced by electrophoretic deposition improved the mechanical and tribological properties of NiTi alloy for biomedical applications. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2019;19:3804–3810. doi: 10.1166/jnn.2019.16327. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous