Review on effects and mechanisms of plant-derived natural products against breast cancer bone metastasis
- PMID: 39318810
- PMCID: PMC11420494
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37894
Review on effects and mechanisms of plant-derived natural products against breast cancer bone metastasis
Abstract
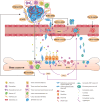
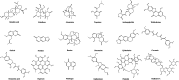
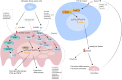
Bone metastasis is the prevalent form of metastasis in breast cancer, resulting in severe pain, pathological fractures, nerve compression, hypercalcemia, and other complications that significantly impair patients' quality of life. The infiltration and colonization of breast cancer (BC) cells in bone tissue disrupt the delicate balance between osteoblasts and osteoclasts within the bone microenvironment, initiating a vicious cycle of bone metastasis. Once bone metastasis occurs, conventional medical therapy with bone-modifying agents is commonly used to alleviate bone-related complications and improve patients' quality of life. However, the utilization of bone-modifying agents may cause severe drug-related adverse effects. Plant-derived natural products such as terpenoids, alkaloids, coumarins, and phenols have anti-tumor, anti-inflammatory, and anti-angiogenic pharmacological properties with minimal side effects. Certain natural products that exhibit both anti-breast cancer and anti-bone metastasis effects are potential therapeutic agents for breast cancer bone metastasis (BCBM). This article reviewed the effects of plant-derived natural products against BCBM and their mechanisms to provide a reference for the research and development of drugs related to BCBM.
Keywords: Bone metastasis; Breast cancer; Mechanism; Natural products; Signaling pathway.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Heterogeneity of tumor cells in the bone microenvironment: Mechanisms and therapeutic targets for bone metastasis of prostate or breast cancer.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2016 Apr 1;99(Pt B):206-211. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2015.11.017. Epub 2015 Dec 4. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2016. PMID: 26656603 Review.
-
Bone Metastasis of Breast Cancer.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1152:105-129. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-20301-6_7. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019. PMID: 31456182 Review.
-
Bone Metastasis of Breast Cancer: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Nov 22;14(23):5727. doi: 10.3390/cancers14235727. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36497209 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Predictive and prognostic biomarkers of bone metastasis in breast cancer: current status and future directions.Cell Biosci. 2023 Dec 1;13(1):224. doi: 10.1186/s13578-023-01171-8. Cell Biosci. 2023. PMID: 38041134 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metastasis of breast cancer to bones alters the tumor immune microenvironment.Eur J Med Res. 2023 Mar 13;28(1):119. doi: 10.1186/s40001-023-01083-w. Eur J Med Res. 2023. PMID: 36915210 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Impact of targeting the platelet-activating factor and its receptor in cancer treatment.Mil Med Res. 2025 Mar 4;12(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s40779-025-00597-0. Mil Med Res. 2025. PMID: 40033370 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Delrieu L., Perol O., Fervers B., Friedenreich C., Vallance J., Febvey-Combes O., et al. A personalized physical activity program with activity trackers and a mobile phone app for patients with metastatic breast cancer: protocol for a single-arm feasibility trial. JMIR Res Protoc. 2018;7 doi: 10.2196/10487. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

