Extraction and Reimplantation of a Subcutaneous Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator: Two Cases and a Review of the Literature
- PMID: 39318900
- PMCID: PMC11421584
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.67737
Extraction and Reimplantation of a Subcutaneous Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator: Two Cases and a Review of the Literature
Abstract
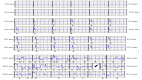
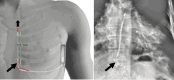
For several years, implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs) have been the cornerstone for the prevention of sudden cardiac death. However, the weakness of traditional transvenous ICD systems lies in the intravascular lead, which is prone to issues such as conductor fracture, insulation abrasion, risk of dislodgement, and infection. With the new generation of subcutaneous defibrillators, these risks are far less common. To date, the frequency of lead fracture is very low, and infection is much rarer. The management of these complications requires complete lead extraction. Traction is the reference procedure, sometimes necessitating the use of a dilating sheath. These techniques remain straightforward to perform without significant risk of procedural complications. Nevertheless, they must be carried out by an expert in cardiac pacing. We report here two cases with indications for lead extraction: one for lead dysfunction and the other for an infection related to a replacement procedure. The management approaches will be described, followed by a review of the literature.
Keywords: infection; lead extraction; lead fracture; subcutaneous implantable cardioverter defibrillator; traction.
Copyright © 2024, Moini et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: All authors have confirmed that this study did not involve human participants or tissue. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Non-traditional implantable cardioverter-defibrillator configurations and insertion techniques: a review of contemporary options.Europace. 2022 Feb 2;24(2):181-192. doi: 10.1093/europace/euab178. Europace. 2022. PMID: 34453529 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Subcutaneous implantable cardioverter defibrillator indication in prevention of sudden cardiac death in difficult clinical situations: A French expert position paper.Arch Cardiovasc Dis. 2020 May;113(5):359-366. doi: 10.1016/j.acvd.2020.03.011. Epub 2020 Apr 22. Arch Cardiovasc Dis. 2020. PMID: 32334981 Review.
-
Efficacy and Complications of Subcutaneous versus Conventional Cardioverter Defibrillators: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Curr Cardiol Rev. 2022;18(3):e081221198647. doi: 10.2174/1573403X17666211208100151. Curr Cardiol Rev. 2022. PMID: 34879809 Free PMC article.
-
Subcutaneous Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator Lead Dislodgement Masquerading as Left Shoulder Pain.Cureus. 2023 Aug 13;15(8):e43435. doi: 10.7759/cureus.43435. eCollection 2023 Aug. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37711957 Free PMC article.
-
Transvenous extraction of implantable cardioverter-defibrillator leads under advisory--a comparison of Riata, Sprint Fidelis, and non-recalled implantable cardioverter-defibrillator leads.Heart Rhythm. 2013 Oct;10(10):1444-50. doi: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2013.06.021. Epub 2013 Jun 28. Heart Rhythm. 2013. PMID: 23816440
References
-
- Annual rate of transvenous defibrillation lead defects in implantable cardioverter-defibrillators over a period of >10 years. Kleemann T, Becker T, Doenges K, et al. https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.663807. Circulation. 2007;115:2474–2480. - PubMed
-
- ANSM. Information de sécurité - défibrillateur implantable sous-cutané. ANSM. 2021. https://ansm.sante.fr/informations-de-securite/defibrillateur-implantabl... https://ansm.sante.fr/informations-de-securite/defibrillateur-implantabl...
-
- Product Performance Report - Boston Scientific. Boston Scientific. Product performance report. 2023. https://www.bostonscientific.com/en-US/pprc/product-performance-report.html https://www.bostonscientific.com/en-US/pprc/product-performance-report.html
-
- Flatline on the alternate vector … is this subcutaneous implantable cardiac defibrillator lead fractured? O’Neill L, Gillis K, Wielandts JY, et al. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2214027121001676 Heart Rhythm Case Rep. 2021;7:758–761. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fracture of an S-ICD lead after two prior transvenous lead-related complications with conventional defibrillators. Gutleben KJ, Nelovic V, Pujdak K, Werner M, Osmani I, Kähler J. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/pace.14101. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2020;43:1491–1494. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
