The Matrix Approach to Patellar Instability
- PMID: 39318946
- PMCID: PMC11421946
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.67703
The Matrix Approach to Patellar Instability
Abstract
Patellar instability is a challenging orthopedic condition affecting both pediatric and adult populations. The diagnosis and treatment of this condition present challenges for surgeons because of the multitude of classifications and treatment options available in the literature, leading to potential confusion in treatment strategies. Nonoperative treatments often prove ineffective, with reported recurrence rates nearing. Consequently, numerous surgical interventions have been developed in pursuit of improved outcomes. However, the results of these early interventions have not been universally successful, resulting in over 100 surgical interventions being recommended for patellofemoral instability, and none of which have achieved universal success. This hesitancy among surgeons to recommend surgery can leave patients inadequately treated. This article aims to share our matrix approach to patellar instability, developed over the past decade. By providing insights into the condition, we hope to stimulate interest among aspiring surgeons and facilitate a comprehensive understanding of the diagnosis and management of patellofemoral instability.
Keywords: dislocation; matrix approach; patella; patellofemoral instability; subluxation.
Copyright © 2024, Almessabi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Animal subjects: All authors have confirmed that this study did not involve animal subjects or tissue. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures





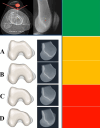


Similar articles
-
Prevailing disagreement in the treatment of complex patellar instability cases: an online expert survey of the AGA Knee-Patellofemoral Committee.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2020 Aug;28(8):2697-2705. doi: 10.1007/s00167-020-05936-3. Epub 2020 Mar 17. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2020. PMID: 32185453
-
Patellar Instability Management: A Survey of the International Patellofemoral Study Group.Am J Sports Med. 2018 Nov;46(13):3299-3306. doi: 10.1177/0363546517732045. Epub 2017 Oct 6. Am J Sports Med. 2018. PMID: 28985094
-
Management of the First Patellar Dislocation: A Narrative Review.Joints. 2019 Dec 31;7(3):107-114. doi: 10.1055/s-0039-3401817. eCollection 2019 Sep. Joints. 2019. PMID: 34195538 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interdisciplinary Orthopedic Management of Pediatric Patella Dislocation and Instability: An Educational Case Series.Cureus. 2023 Aug 2;15(8):e42860. doi: 10.7759/cureus.42860. eCollection 2023 Aug. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37664368 Free PMC article.
-
Pediatric Management of Recurrent Patellar Instability.Sports Med Arthrosc Rev. 2019 Dec;27(4):171-180. doi: 10.1097/JSA.0000000000000256. Sports Med Arthrosc Rev. 2019. PMID: 31688538 Review.
References
-
- Predictors of recurrent instability after acute patellofemoral dislocation in pediatric and adolescent patients. Lewallen LW, McIntosh AL, Dahm DL. Am J Sports Med. 2013;41:575–581. - PubMed
-
- Medial patellofemoral ligament: anatomy, injury and treatment in the adolescent knee. Hensler D, Sillanpaa PJ, Schoettle PB. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2014;26:70–78. - PubMed
-
- Correlations between intra and extraarticular factors measured by computed tomography in patients with recurrent patellar dislocation. Iacobescu G, Cursaru A, Anghelescu D, Popa M, Popescu D. Rom J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2020;3:20–28.
-
- Alshryda S, Tsang K, De Kiewiet G. Paediatric Orthopaedics: An Evidence-Based Approach to Clinical Questions, 1st Edition. Cham, Switzerland: Springer; 2017. Evidence-based treatment for slipped upper femoral epiphysis; pp. 51–70.
-
- Epidemiology and natural history of acute patellar dislocation. Fithian DC, Paxton EW, Stone ML, Silva P, Davis DK, Elias DA, White LM. Am J Sports Med. 2004;32:1114–1121. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
