Epidemiology of Periodontal Diseases in Individuals With Diabetes in Saudi Arabia: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 39318963
- PMCID: PMC11421309
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.67721
Epidemiology of Periodontal Diseases in Individuals With Diabetes in Saudi Arabia: A Systematic Review
Abstract
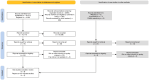
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is one of the most common and prevalent metabolic disorders worldwide. It affects men, women, and children and can cause severe organ damage, including kidney damage. The two most common types of DM are Type 1 DM and Type 2 DM. Similarly, periodontal disease (PD) affects a significant portion of the population and involves the tissues supporting the teeth. The bidirectional relationship between diabetes and PD is a well-established phenomenon. However, no comprehensive study on the prevalence of PD among diabetic patients has been conducted on the Saudi population. This systematic review aims to examine the current literature on the impact of these conditions on the Saudi population. A literature search was conducted from January 2001 through June 2024 using Scopus, PubMed, and Google Scholar. An extensive search was performed, duplicates were removed, and inclusion and exclusion criteria were applied. Nine studies were selected for review, adhering to Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines. The retrieved studies confirm the relationship between DM and PDs in regional studies. The review highlights the need for integrated healthcare approaches to manage both conditions effectively. Further research is recommended to understand the causal mechanisms and develop comprehensive treatment strategies.
Keywords: diabetes mellitus type 2; gingivitis; periodontal diseases; periodontitis; type 1 diabetes mellitus (t1d).
Copyright © 2024, AlJaafary et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association between Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus and Periodontal Diseases.J Clin Med. 2023 Feb 1;12(3):1147. doi: 10.3390/jcm12031147. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 36769794 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Prevalence of Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Patients With Diabetes Mellitus in Yemen: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Cureus. 2024 Nov 1;16(11):e72848. doi: 10.7759/cureus.72848. eCollection 2024 Nov. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39618736 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beyond the black stump: rapid reviews of health research issues affecting regional, rural and remote Australia.Med J Aust. 2020 Dec;213 Suppl 11:S3-S32.e1. doi: 10.5694/mja2.50881. Med J Aust. 2020. PMID: 33314144
-
The burden of Diabetes, Its Oral Complications and Their Prevention and Management.Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2018 Aug 15;6(8):1545-1553. doi: 10.3889/oamjms.2018.294. eCollection 2018 Aug 20. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2018. PMID: 30159091 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Magnitude of diabetic peripheral neuropathy in Saudi Arabia: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Endocr Disord. 2022 Nov 2;22(1):266. doi: 10.1186/s12902-022-01167-4. BMC Endocr Disord. 2022. PMID: 36319996 Free PMC article.
References
-
- A brief overview of diabetes. Shivashankar M, Mani D. https://web.archive.org/web/20180412210827id_/http://ijppsjournal.com/Vo... Int J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2011;3:22–27.
-
- General aspects of diabetes mellitus. Alam U, Asghar O, Azmi S, Malik RA. Handb Clin Neurol. 2014;126:211–222. - PubMed
-
- Periodontal diseases. Kinane DF, Stathopoulou PG, Papapanou PN. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3:17038. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous