Validation of behavioral measures of social cognition in individuals diagnosed with schizophrenia
- PMID: 39319067
- PMCID: PMC11420990
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1443145
Validation of behavioral measures of social cognition in individuals diagnosed with schizophrenia
Abstract
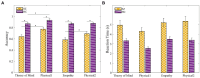
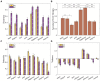
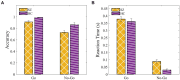
Schizophrenia, a complex neuropsychiatric disorder, manifests severe impairments in social cognition, notably in Theory of Mind (ToM), empathy, and emotion recognition, which significantly influence social competence and overall functioning. These aspects are crucial for prognosis in individuals diagnosed with schizophrenia (SZ). This study validates a comics strip paradigm for ToM and empathy assessment, the Montreal Affective Voices (MAV) for measuring emotion recognition, and a Go-NoGo task for inhibition control estimation in individuals diagnosed with SZ, comparing their performance with healthy controls. SZ participants exhibited diminished abilities in the comics strip task, especially in ToM and empathy conditions, alongside challenges in identifying emotions from vocal cues in MAV. They responded slower and tended to be less accurate in the Go-NoGo task. The validated behavioral battery addresses the limitations of previous measures and emerges as a promising tool for future investigations into the neural systems underlying social cognition in schizophrenia. Such insights can lead to the development of long-needed treatment for negative symptoms and social dysfunctions in schizophrenia.
Keywords: Go-NoGo; Montreal Affective Voices (MAV); comic strip; emotion recognition; schizophrenia; social cognition; theory of mind (ToM).
Copyright © 2024 Rahamim, Gilad, Linkovski, Bergman, Avirame, Foul and Eitan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Differences between individuals with schizophrenia or obsessive-compulsive disorder and healthy controls in social cognition and mindfulness skills: A controlled study.PLoS One. 2019 Dec 11;14(12):e0225608. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0225608. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31825973 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Emotion perception, non-social cognition and symptoms as predictors of theory of mind in schizophrenia.Compr Psychiatry. 2018 Aug;85:1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.comppsych.2018.05.002. Epub 2018 Jun 5. Compr Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 29906670
-
Social cognition and psychosocial functioning in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder: Theory of mind as a key to understand schizophrenia dysfunction.Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2023 Dec;77:12-20. doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2023.08.483. Epub 2023 Sep 1. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37660439
-
[Social cognition in schizophrenia and autism spectrum disorder: Points of convergence and functional differences].Encephale. 2018 Dec;44(6):523-537. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2018.03.004. Epub 2018 Aug 16. Encephale. 2018. PMID: 30122298 Review. French.
-
[Disturbances of social cognition in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder--similarities and differences].Psychiatr Pol. 2014 May-Jun;48(3):515-26. Psychiatr Pol. 2014. PMID: 25204097 Review. Polish.
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association . (2013). Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. American Psychiatric Association.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

