Mechanism of Mongolian mind-body interactive therapy in regulating essential hypertension through HTR2B: A metabolome- and transcriptome-based study
- PMID: 39319128
- PMCID: PMC11419866
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37113
Mechanism of Mongolian mind-body interactive therapy in regulating essential hypertension through HTR2B: A metabolome- and transcriptome-based study
Abstract
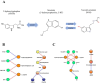
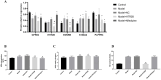
Essential hypertension is a psychosomatic disease associated with emotions and behaviors. Although Mongolian mind-body interactive therapy can help patients with essential hypertension reduce their systolic blood pressure (SBP), the mechanism is unclear. We assigned patients who underwent Mongolian mind-body interactive therapy to groups that were treated with (DT) or without (NDT) antihypertensive drugs (Clinical registration no: ChiCTR2000034918). We screened differentially expressed genes (DEGs) using targeted metabolic and transcriptomic analyses of blood samples before and after intervention. Sequenced data were analyzed using quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) and validated using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs). Small interfering (Si)-RNA interference on key DEGs in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) was experimentally verified. Omics analysis identified 187 DEGS, including human 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) receptor 2B (5-HTR2B), human endothelin receptor type B (EDNRB), and the metabolite N-acetylserotonin. The qPCR and transcriptome sequencing results were consistent. Post-intervention ELISA assays revealed significantly elevated 5-HT in the NDT group after intervention (P < 0.05). Interactions between 5-HTR2B and N-acetylserotonin differed between the groups. The cellular findings showed significantly reduced G protein-coupled receptor 82 (GPR82) and phospholipid phosphatase-related protein type 4 (PLPPR4), and significantly increased S100A2 protein expression in the Si-HTR2B group, compared with the controls (P < 0.05). The biochemical results uncovered significantly decreased nitric oxide (NO) and significantly increased malondialdehyde and NO synthetase concentrations compared with the models (P < 0.05). Mongolian mind-body interactive therapy might affect SBP in patients with essential hypertension by combining 5-HT with 5-HTR2B to mediate NO relaxation.
Keywords: 5-Hydroxytryptamine; 5-Hydroxytryptamine receptor 2B; Essential hypertension; Mongolian mind–body interactive therapy; N-acetylserotonin.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
On behalf of all the authors, I declare that no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Increased Serotonin Signaling Contributes to the Warburg Effect in Pancreatic Tumor Cells Under Metabolic Stress and Promotes Growth of Pancreatic Tumors in Mice.Gastroenterology. 2017 Jul;153(1):277-291.e19. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.03.008. Epub 2017 Mar 15. Gastroenterology. 2017. PMID: 28315323
-
New Method for Insomnia Mongolian Mind-Body Interactive Psychotherapy in the Assessment of Chronic Insomnia: A Retrospective Study.Adv Ther. 2018 Jul;35(7):993-1000. doi: 10.1007/s12325-018-0726-9. Epub 2018 Jun 19. Adv Ther. 2018. PMID: 29923046 Free PMC article.
-
SP1 transcriptionally activates HTR2B to aggravate traumatic spinal cord injury by shifting microglial M1/M2 polarization.J Orthop Surg Res. 2024 Apr 8;19(1):230. doi: 10.1186/s13018-024-04678-z. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024. PMID: 38589918 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of HTR2B-mediated serotonin signaling in colorectal cancer suppresses tumor growth through ERK signaling.Biomed Pharmacother. 2024 Oct;179:117428. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.117428. Epub 2024 Sep 9. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 39255737
-
Dissecting the novel abilities of aripiprazole: The generation of anti-colorectal cancer effects by targeting Gαq via HTR2B.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2023 Aug;13(8):3400-3413. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2023.05.015. Epub 2023 May 19. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2023. PMID: 37655314 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Polcari J.J., Cali R.J., Nephew B.C., Lu S., Rashkovskii M., Wu J., Saadeh F., Loucks E., King J.A. Effects of the Mindfulness-Based Blood Pressure Reduction (MB-BP) program on depression and neural structural connectivity. J. Affect. Disord. 2022;311:31–39. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2022.05.059. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chambra: Mongolian Medicine Jinkui. Department of Mongolian Medicine and Fuxin Mongolian People's Hospital of Bameng Linhe. 1977.P13-16.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

