Effectiveness of a single dose of JYNNEOS vaccine in real world: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 39319246
- PMCID: PMC11420512
- DOI: 10.1002/hsr2.70069
Effectiveness of a single dose of JYNNEOS vaccine in real world: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Mpox infection is a zoonotic illness that resembles smallpox. Vaccination is widely regarded as a vital effective method of preventing mpox, however, there is lack of consensus of effectiveness of a single dose of mpox vaccine in the current 2022-2023 outbreak. We pooled data from real-world studies to evaluate the efficacy of the JYNNEOS vaccination given as a single dosage.
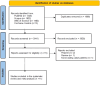
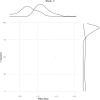
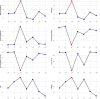
Method: We carried out a thorough literature search in PubMed, Web of Science, and Scopus up until August 2023. We estimated the pooled vaccine effectiveness (VE) for mpox using inverse variance method in a random-effects meta-analysis. We expressed the results as VE, 95% confidence interval (95% CI), and 95% prediction interval (95% PI) using R v4.3.0. We assessed influence, heterogeneity contribution, and influence of studies using several tests and conducted sensitivity analysis accordingly. We used Doi plot and Luis Furuya-Kanamori (LFK) index to evaluate publication bias.
Results: With a total sample size of 35,326 individuals, we involved 11 studies in the meta-analysis. The VE of a single dose of JYNNEOS vaccine was 78.23% (95% CI: 62.79%-87.27%) by pooling data of 24,784 individuals over seven studies. The findings were heterogenous with a 95% PI of -32.14% to 96.41% depicting the expected range of VE in similar settings. Notably, VE increased to 83.02% (74.62%-88.64%) with a prediction interval of (44.67%-94.79) after sensitivity analysis by leaving out outliers. The results were robust in light of several sensitivity analyses. An asymmetric Doi plot with LFK index of -2.25 showed potential publication bias. Pooled prevalence of mpox infection among vaccinated individuals (breakthrough infection) in six studies was 2.19% (0.37%-5.32%).
Conclusion: The present findings provide compelling evidence that a single dose of JUNNEOS vaccine can protect recipients from mpox infection. With a 78.23% estimated efficacy rate, the vaccine is thought to be a useful tool in preventing further spread of mpox. However, more research and ongoing surveillance are required to fully understand the reasons behind breakthrough infections and to improve immunization strategies for better protection against mpox.
Keywords: JYNNEOS; MPXV; Mpox: vaccine; effectiveness.
© 2024 The Author(s). Health Science Reports published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declares no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effectiveness of JYNNEOS vaccine against symptomatic mpox disease in adult men in Los Angeles County, August 29, 2022 to January 1, 2023.Vaccine. 2024 Aug 13;42(20):125987. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2024.05.035. Epub 2024 May 24. Vaccine. 2024. PMID: 38789368
-
Estimated Effectiveness of JYNNEOS Vaccine in Preventing Mpox: A Multijurisdictional Case-Control Study - United States, August 19, 2022-March 31, 2023.MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023 May 19;72(20):553-558. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7220a3. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023. PMID: 37200229 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of JYNNEOS Vaccine Against Diagnosed Mpox Infection - New York, 2022.MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023 May 19;72(20):559-563. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7220a4. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023. PMID: 37339074 Free PMC article.
-
Proctitis and Other Gastrointestinal Manifestations in Mpox Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.JGH Open. 2025 May 28;9(6):e70190. doi: 10.1002/jgh3.70190. eCollection 2025 Jun. JGH Open. 2025. PMID: 40444185 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MVA-BN vaccine effectiveness: A systematic review of real-world evidence in outbreak settings.Vaccine. 2024 Dec 2;42(26):126409. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2024.126409. Epub 2024 Oct 16. Vaccine. 2024. PMID: 39413490
Cited by
-
Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of Peruvian patients with mpox: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2025 Jun 25;20(6):e0327097. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0327097. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40561075 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shchelkunov SN, Marennikova SS, Moyer RW. Orthopoxviruses Pathogenic for Humans. Springer Science & Business Media; 2006.
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . Past U.S. cases and outbreaks.2022.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

