Regenerative potential of mouse neonatal intervertebral disc depends on collagen crosslink density
- PMID: 39319260
- PMCID: PMC11421255
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110883
Regenerative potential of mouse neonatal intervertebral disc depends on collagen crosslink density
Abstract
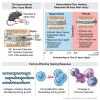
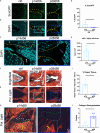
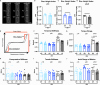
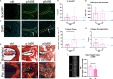
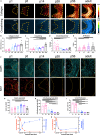
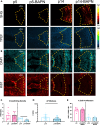
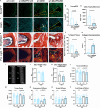
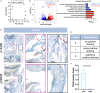
Intervertebral disc (IVD) defects heal poorly and can cause back pain and disability. We identified that IVD herniation injury heals regeneratively in neonatal mice until postnatal day 14 (p14) and shifts to fibrotic healing by p28. This age coincides with the shift in expansive IVD growth from cell proliferation to matrix elaboration, implicating collagen crosslinking. β-aminopropionitrile treatment reduced IVD crosslinking and caused fibrotic healing without affecting cell proliferation. Bulk sequencing on naive IVDs was depleted for matrix structural organization from p14 to p28 to validate the importance of crosslinking in regenerative healing. We conclude that matrix changes are key drivers in the shift to fibrotic healing, and a stably crosslinked matrix is needed for IVD regeneration.
Keywords: Molecular biology; Omics; Tissue Engineering; Transcriptomics.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Iatridis J.C., Nicoll S.B., Michalek A.J., Walter B.A., Gupta M.S. Role of biomechanics in intervertebral disc degeneration and regenerative therapies: what needs repairing in the disc and what are promising biomaterials for its repair? Spine J. 2013;13:243–262. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2012.12.002. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

