Blind Brush Biopsy: Quantification of Epstein-Barr Virus and Its Host DNA Methylation in the Detection of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
- PMID: 39319346
- PMCID: PMC11420652
- DOI: 10.34133/research.0475
Blind Brush Biopsy: Quantification of Epstein-Barr Virus and Its Host DNA Methylation in the Detection of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
Abstract
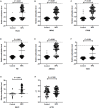
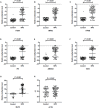
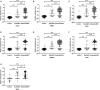
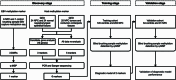
Background: The nasopharyngeal brush sampling can effectively collect samples from the nasopharynx. The blind brush sampling does not require the guidance of endoscopy, which is favorable for implementation and dissemination in the community. This study explored methylation markers for nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) at both Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) and its host genome levels, aiming to construct a blind brushing diagnostic method. Methods: EBV DNA capture and methylation sequencing and GEO Illumina 450K methylation array data were used respectively for the discovery of EBV and host methylation markers. The diagnostic method was built in training cohort (n = 347) and validated in an independent validation cohort (n = 155). Results: A total of 1 EBV methylation marker (BILF2) and 6 host methylation markers (ITGA4, IMPA2, ITPKB, PI9, AMIGO2, and VAV3) were identified. Both EBV and host methylation markers were almost exclusively detected in NPC samples, with negligible detection in control samples. In validation cohort, the diagnostic method that included only the EBV BILF2 marker showed a sensitivity and specificity of 80.22% and 98.44%, respectively. When combining the EBV-derived marker BILF2 with the host-derived marker IMPA2, the diagnostic method's sensitivity increased to 84.62%, while the specificity remained unchanged (IDI = 4.4%, P = 0.0419). Conclusion: Overall, the blind nasopharyngeal brushing diagnostic method, combining EBV and host methylation markers, showed great potential in NPC detection and could promote its application in nonclinical screening of NPC.
Copyright © 2024 Caoli Tang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Quantitative detection of Epstein-Barr virus DNA methylation in the diagnosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by blind brush sampling.Int J Cancer. 2023 Jun 15;152(12):2629-2638. doi: 10.1002/ijc.34491. Epub 2023 Mar 13. Int J Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36878711
-
Detection of methylation status of Epstein-Barr virus DNA C promoter in the diagnosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Cancer Sci. 2020 Feb;111(2):592-600. doi: 10.1111/cas.14281. Epub 2020 Feb 5. Cancer Sci. 2020. PMID: 31834989 Free PMC article.
-
Quantification of Epstein-Barr virus DNA load in nasopharyngeal brushing samples in the diagnosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma in southern China.Cancer Sci. 2015 Sep;106(9):1196-201. doi: 10.1111/cas.12718. Epub 2015 Jul 14. Cancer Sci. 2015. PMID: 26082292 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in Assessing the Clinical Implications of Epstein-Barr Virus Infection and Their Application to the Diagnosis and Treatment of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma.Microorganisms. 2023 Dec 20;12(1):14. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12010014. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 38276183 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical utility of circulating Epstein-Barr virus DNA analysis for the management of nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Chin Clin Oncol. 2016 Apr;5(2):18. doi: 10.21037/cco.2016.03.07. Chin Clin Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27121878 Review.
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209–249. - PubMed
-
- Yip TTC, Ngan RKC, Fong AHW, Law SCK. Application of circulating plasma/serum EBV DNA in the clinical management of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2014;50(6):527–538. - PubMed
-
- Ji MF, Sheng W, Cheng WM, Ng MH, Wu BH, Yu X, Wei KR, Li FG, Lian SF, Wang PP, et al. . Incidence and mortality of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Interim analysis of a cluster randomized controlled screening trial (PRO-NPC-001) in southern China. Ann Oncol. 2019;30(10):1630–1637. - PubMed
-
- Li T, Li F, Guo X, Hong C, Yu X, Wu B, Lian S, Song L, Tang J, Wen S, et al. . Anti–Epstein–Barr virus BNLF2b for mass screening for nasopharyngeal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2023;389(9):808–819. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

