Quantitative MRI for Monitoring Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: A Test-Retest Repeatability Study
- PMID: 39319470
- PMCID: PMC11896917
- DOI: 10.1002/jmri.29610
Quantitative MRI for Monitoring Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: A Test-Retest Repeatability Study
Abstract
Background: Quantitative magnetic resonance imaging metrics iron-corrected T1 (cT1) and liver fat from proton density fat-fraction (PDFF) are both commonly used as noninvasive biomarkers for metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH); however, their repeatability in this population has rarely been characterized.
Purpose: To quantify the variability of cT1 and liver fat fraction from PDFF in patients with biopsy-confirmed metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) and MASH.
Study type: Prospective, single center.
Population: Twenty-one participants (female = 11, mean age 53 ± 24 years) with biopsy-confirmed MASLD, including 6 with MASH and fibrosis ≥2.
Field strength/sequence: 3 T; T1 and T2* mapping for the generation of cT1 (shMOLLI: CardioMaps and 2D MDE, T1map-FIESTA and LMS MOST: StarMap, 2D Multi-Echo FSPGR) and magnitude-only PDFF sequence for liver fat quantification (LMS IDEAL: StarMap, 2D Multi-Echo FSPGR).
Assessment: T1 mapping and PDFF scans were performed twice on the same day for all participants (N = 21), with an additional scan 2-4 weeks later for MASH patients with fibrosis ≥2 (N = 6). Whole liver segmentation masks were generated semi-automatically and average pixel counts within these masks were used for the calculation of cT1 and liver fat fraction.
Statistical tests: Bland-Altman analysis for repeatability coefficient (RC) and 95% limits of agreement (LOA) and intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC).
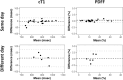
Results: Same-day RC was 32.1 msec (95% LOA: -36.6 to 24.2 msec) for cT1 and 0.6% (95% LOA: -0.5% to 0.7%) for liver fat fraction; the ICCs were 0.98 (0.96-0.99) and 1.0, respectively. Short-term RC was 65.2 msec (95% LOA: -63.8 to 76.5 msec) for cT1 and 2.6% (95% LOA: -2.8% to 3.1%) for liver fat fraction.
Data conclusion: In participants with MASLD and MASH, cT1 and liver fat fraction measurements show excellent test-retest repeatability, supporting their use in monitoring MASLD and MASH.
Level of evidence: 2 TECHNICAL EFFICACY: Stage 2.
Keywords: MASH; MASLD; PDFF; cT1; multiparametric‐MRI.
© 2024 The Author(s). Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
Cayden Beyer, Anneli Andersson, Elizabeth Shumbayawonda, and Andrea Dennis are all employees of Perspectum. Naim Alkhouri, Mukesh Harisinghani, and Michele Pansini are consultants for Perspectum.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Head-to-head comparison among FAST, MAST, and multiparametric MRI-based new score in diagnosing at-risk MASH.Eur Radiol. 2025 Jun;35(6):3599-3609. doi: 10.1007/s00330-024-11215-3. Epub 2024 Dec 5. Eur Radiol. 2025. PMID: 39638942 Clinical Trial.
-
The effectiveness of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) iron corrected T1 in monitoring metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis in obesity following bariatric surgery and lifestyle modification: a prospective cohort study.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024 Jul 1;14(7):4659-4674. doi: 10.21037/qims-24-148. Epub 2024 May 24. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024. PMID: 39022255 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound-Derived Fat Fraction for Hepatic Steatosis Assessment: Prospective Study of Agreement With MRI PDFF and Sources of Variability in a Heterogeneous Population.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2024 Jun;222(6):e2330775. doi: 10.2214/AJR.23.30775. Epub 2024 Jun 12. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2024. PMID: 38506537
-
Clinical Utility of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Biomarkers for Identifying Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Patients at High Risk of Progression: A Multicenter Pooled Data and Meta-Analysis.Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Nov;20(11):2451-2461.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2021.09.041. Epub 2021 Oct 7. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 34626833 Review.
-
Application and research progress of magnetic resonance proton density fat fraction in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: a comprehensive review.Abdom Radiol (NY). 2025 Jan;50(1):185-197. doi: 10.1007/s00261-024-04448-9. Epub 2024 Jul 24. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2025. PMID: 39048719 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

