Kinetics and Prognosis Value of CCL5/RANTES at the Acute Phase of ST-Segment-Elevation Myocardial Infarction
- PMID: 39319665
- PMCID: PMC11681460
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.123.033110
Kinetics and Prognosis Value of CCL5/RANTES at the Acute Phase of ST-Segment-Elevation Myocardial Infarction
Abstract
Background: RANTES (regulated upon activation, normal T cell expressed, and secreted) or CCL5 (CC chemokine ligand 5) is a chemokine that mediates chemotaxis and activation of T cells, monocytes, mast cells, and dendritic cells. It is involved in the pathogenesis of several diseases, including atherosclerosis, but its role at the acute phase of myocardial infarction (MI) is unclear. Our objective is to determine whether the serum level of RANTES is a marker of the severity of acute MI.
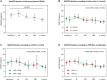
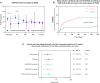
Methods and results: The study included 250 consecutive patients with ST-segment-elevation MI who underwent percutaneous coronary intervention in a prospective cohort. Peripheral venous blood samples were taken at 5 time points and ELISA was performed. Major adverse cardiovascular events were prospectively recorded over the 12-month follow-up. Serum RANTES level raised from 12.9 (8.0-20.7) ng/mL at H0 to 13.9 (7.4-22.4) ng/mL at H4 and decreased gradually until 1 month at 9.7 (5.4-13.6) ng/mL (P<0.0001). RANTES area under the curve (AUC) level was not correlated with infarct size (r=-0.03, P=0.70) or left ventricular ejection fraction assessed by magnetic resonance imaging (r=0.02, P=0.80). Patients with a RANTES AUC serum level below the first tertile value of the population (411.0 ng.h.mL-1) were more likely to have a major adverse cardiovascular event during the first 12 months after ST-segment-elevation MI (hazard ratio [HR], 2.9 [1.3-6.6], P=0.01). In a multivariable Cox regression analysis, serum level below the first tertile remained associated with an increased risk of experiencing major adverse cardiovascular event during the follow-up (adjusted HR, 2.6 [1.2-5.8], P=0.02).
Conclusions: A low level of circulating RANTES post ST-segment-elevation MI was associated with an increased risk of experiencing major adverse cardiovascular event and might be a valuable prognostic marker in patients with ST-segment-elevation MI.
Keywords: ELISA; biomarker; myocardial infarction; systemic inflammation.
Figures
Comment in
-
Younger Women With Myocardial Infarction: Where Are the Cracks in the System?J Am Heart Assoc. 2024 Oct;13(19):e037479. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.124.037479. Epub 2024 Sep 25. J Am Heart Assoc. 2024. PMID: 39319477 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Herder C, Peeters W, Illig T, Baumert J, De Kleijn DPV, Moll FL, Poschen U, Klopp N, Müller‐Nurasyid M, Roden M, et al. RANTES/CCL5 and risk for coronary events: results from the MONICA/KORA Augsburg Case‐Cohort, athero‐Express and CARDIoGRAM studies. Song Y, ed. PLoS One. 2011;6:e25734. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Montecucco F, Braunersreuther V, Lenglet S, Delattre BMA, Pelli G, Buatois V, Guilhot F, Galan K, Vuilleumier N, Ferlin W, et al. CC chemokine CCL5 plays a central role impacting infarct size and post‐infarction heart failure in mice. Eur Heart J. 2012;33:1964–1974. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehr127 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

