Combined Forehead and Temporal Lifting: An Innovative Approach to Lanluma V Treatment
- PMID: 39319782
- PMCID: PMC11743029
- DOI: 10.1111/jocd.16583
Combined Forehead and Temporal Lifting: An Innovative Approach to Lanluma V Treatment
Abstract
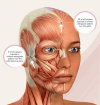
Background: Excess skin laxity over the upper face can contribute to aging over the mid and lower face. We describe an innovative nonsurgical technique of facial rejuvenation by injecting Lanluma V over the scalp's vertex and parietal regions. Lanluma V is a poly-l-lactic acid (PLLA)-based collagen stimulator which contains 210 mg of PLLA, distributed by Sinclair Pharmaceutical. Lanluma V works by stimulating collagen regeneration to provide support for the treated area.
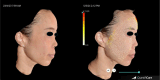
Method: A retrospective review of 12 consecutive patients treated with Lanluma V over the vertex and parietal regions of the scalp to achieve nonsurgical rejuvenation of the upper, middle, and lower thirds of the face was conducted. The patients were treated over two sessions, 1 month apart. The treated patients were reviewed by a plastic surgeon and rated under the Global Aesthetic Improvement Scale (GAIS) 6 months after treatment.
Results: The patients achieved an overall average of 1.16 grade improvement in GAIS. The average follow-up period is 6 months following completion of treatment. There was no reported incidence of non-scarring alopecia, which has been reported in the use of other, more viscous fillers such as calcium hydroxyapatite or high G' hyaluronic acid.
Conclusion: This innovative method of combined forehead and temporal lifting with Lanluma V allows for an average 1.16 grade improvement in GAIS. There is no reported incidence of non-scarring alopecia, which has been associated with other fillers.
Keywords: Global Aesthetic Improvement Scale; Lanluma V; forehead lift; nonsurgical facial rejuvenation; non‐scarring alopecia; poly‐l‐lactic acid; temporal lift.
© 2024 The Author(s). Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Larry Wu: none; Giovanni Salti: Consultant to Sinclair pharmaceutical.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Exploring the Safety and Satisfaction of Patients Injected With Collagen Biostimulators-A Prospective Investigation Into Injectable Poly-l-Lactic Acid (PLLA).J Cosmet Dermatol. 2025 Feb;24(2):e16723. doi: 10.1111/jocd.16723. Epub 2024 Dec 12. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 39663956 Free PMC article.
-
Three Key Submuscular Points for Nonsurgical Rejuvenation of the Midface in Caucasian Patients: A Methodological Approach Using Injectable Hyaluronic Acid Fillers.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2024 Aug;48(16):3154-3162. doi: 10.1007/s00266-024-03921-6. Epub 2024 Mar 12. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2024. PMID: 38472347
-
Enhancing Facial Projection: Efficacy and Safety of a Novel Filler Combining Cross-Linked Sodium Hyaluronate Gel With Poly-L-Lactic Acid-b-PEG Microspheres for T-Zone Augmentation.J Cosmet Dermatol. 2025 Mar;24(3):e70003. doi: 10.1111/jocd.70003. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 40114452 Free PMC article.
-
Collagen Stimulators: Poly-L-Lactic Acid and Calcium Hydroxyl Apatite.Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am. 2015 Nov;23(4):459-69. doi: 10.1016/j.fsc.2015.07.007. Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am. 2015. PMID: 26505542 Review.
-
Injectable Poly-L-Lactic Acid for Body Aesthetic Treatments: An International Consensus on Evidence Assessment and Practical Recommendations.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2025 Mar;49(5):1507-1517. doi: 10.1007/s00266-024-04499-9. Epub 2024 Nov 26. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2025. PMID: 39592491 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Langton A. K., Sherratt M. J., Griffiths C. E. M., and Watson R. E. B., “A New Wrinkle on Old Skin: The Role of Elastic Fibres in Skin Ageing,” International Journal of Cosmetic Science 32, no. 5 (2010): 330–339. - PubMed
-
- Helfrich Y. R., Sachs D. L., and Voorhees J. J., “Overview of Skin Aging and Photoaging,” Dermatology Nursing 20, no. 3 (2008): 177–183. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

