Effects of Thai propolis mixed in mineral trioxide aggregate on matrix metalloproteinase-2 expression and activity in inflamed human dental pulp cells
- PMID: 39319905
- PMCID: PMC11464073
- DOI: 10.1590/1678-7757-2024-0168
Effects of Thai propolis mixed in mineral trioxide aggregate on matrix metalloproteinase-2 expression and activity in inflamed human dental pulp cells
Abstract
Objectives: This study sought to determine effects of Thai propolis extract mixed in mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) on matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) expression and its activity in inflamed human dental pulp cells (HDPCs).
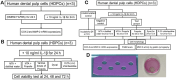
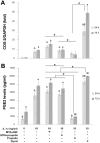
Materials and methods: Interleukin-1β-primed HDPCs were treated with either the eluate of MTA mixed with distilled water, of MTA mixed with 0.75 mg/ml of the propolis extract, or of Dycal®, 0.75 mg/ml of the propolis extract, or 0.2% (v/v) of chlorhexidine for 24 or 72 h. The viability of HDPCs was determined by the PrestoBlue® cytotoxic assay. HDPCs' lysates were analyzed for MMP-2 mRNA expression by RT-qPCR, while their supernatants were measured for MMP-2 activity by gelatin zymography.
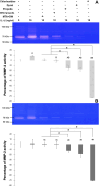
Results: At 24 and 72 h, a non-toxic dose of the propolis extract at 0.75 mg/ml by itself or mixed in MTA tended to reduce MMP-2 expression upregulated by MTA, while it further decreased the MMP-2 activity as compared to that of MTA mixed with distilled water. The MMP-2 activity of interleukin-1β-primed HDPCs treated with the eluate of the propolis extract mixed in MTA was significantly lower than that of interleukin-1β-primed HDPCs at 24 h (p=0.012). As a control, treatment with chlorhexidine significantly inhibited MMP-2 expression induced by MTA and MMP-2 activity enhanced by interleukin-1β (p<0.05). Treatment with Dycal® caused a significant increase in HDPC's death, resulting in a significant decrease in MMP-2 expression and activity (p<0.05).
Conclusions: MTA mixed with Thai propolis extract can reduce MMP-2 mRNA expression and activity when compared to MTA mixed with distilled water in inflamed HDPCs.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effects of MTA and Brazilian propolis on the biological properties of dental pulp cells.Braz Oral Res. 2020 Jan 10;33:e117. doi: 10.1590/1807-3107bor-2019.vol33.0117. eCollection 2020. Braz Oral Res. 2020. PMID: 31939498
-
Role of the p38 pathway in mineral trioxide aggregate-induced cell viability and angiogenesis-related proteins of dental pulp cell in vitro.Int Endod J. 2015 Mar;48(3):236-45. doi: 10.1111/iej.12305. Epub 2014 Jun 25. Int Endod J. 2015. PMID: 24773073
-
Combination of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate and Platelet-rich Fibrin Promotes the Odontoblastic Differentiation and Mineralization of Human Dental Pulp Cells via BMP/Smad Signaling Pathway.J Endod. 2016 Jan;42(1):82-8. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2015.06.019. Epub 2015 Sep 9. J Endod. 2016. PMID: 26364004
-
A comparative study of BioAggregate and ProRoot MTA on adhesion, migration, and attachment of human dental pulp cells.J Endod. 2014 Aug;40(8):1118-23. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2013.12.028. Epub 2014 Feb 5. J Endod. 2014. PMID: 25069918
-
The effect of fluocinolone acetonide, ProRoot MTA and their combination on inflammation and odontogenic differentiation of inflamed human dental pulp cells.Clin Oral Investig. 2025 Jun 26;29(7):358. doi: 10.1007/s00784-025-06380-8. Clin Oral Investig. 2025. PMID: 40562895
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

