Influenza Epidemiology and Vaccine Effectiveness Following Funded Influenza Vaccine in Queensland, Australia, 2022
- PMID: 39320009
- PMCID: PMC11423337
- DOI: 10.1111/irv.70007
Influenza Epidemiology and Vaccine Effectiveness Following Funded Influenza Vaccine in Queensland, Australia, 2022
Abstract
Background: In 2022, publicly funded influenza vaccine was made available to all residents of Queensland, Australia. This study compared influenza epidemiology in 2022 with previous years (2017-2021) and estimated influenza vaccine effectiveness (VE) during 2022.
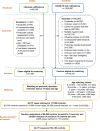
Methods: The study involved a descriptive analysis of influenza notifications and a case-control study to estimate VE. Cases were notifications of laboratory-confirmed influenza, and controls were individuals who were test negative for COVID-19. Cases and controls were matched on age, postcode and specimen collection date. VE against hospitalisation was investigated by matching hospitalised cases to controls. Conditional logistic regression models were adjusted for sex.
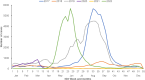
Results: In 2022, Queensland experienced an early influenza season onset (April-May) and high case numbers (n = 45,311), compared to the previous 5 years (annual average: 29,364) and 2020-2021 (2020:6047; 2021:301) during the COVID-19 pandemic. Adjusted VE (VEadj) against laboratory-confirmed influenza was 39% (95% confidence interval [CI]: 37-41), highest for children aged 30 months to < 5 years (61%, 95% CI: 49-70) and lowest for adults aged ≥ 65 years (24%, 95% CI: 17-30). VEadj against influenza-associated hospitalisation was 54% (95% CI: 48-59). Among children < 9 years of age, VEadj against laboratory-confirmed influenza (55%, 95% CI: 49-61) and hospitalisation (67%, 95% CI: 39-82) was higher in those who received a complete dose schedule.
Conclusion: In Queensland, the 2022 influenza season started earlier than the previous 5 years. VE against influenza notifications varied across age groups. VE estimates against influenza-associated hospitalisation were higher than those against laboratory-confirmed influenza.
Keywords: Australia; Queensland; flu; influenza; influenza vaccine; vaccine effectiveness.
© 2024 The Author(s). Influenza and Other Respiratory Viruses published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Australian Government Department of Health and Aged Care , Australian National Notifiable Diseases and Case Definitions (Canberra: Australian Government Department of Health and Aged Care, 2021. (cited 2022 Jun 06). Available from:), https://www1.health.gov.au/internet/main/publishing.nsf/Content/cdna‐cas....
-
- Australian Government Department of Health and Aged Care , National Immunisation Program Schedule (Canberra: Australian Government Department of Health and Aged Care, 2022. (cited 2022 Jun 07). Available from:), https://www.health.gov.au/health‐topics/immunisation/when‐to‐get‐vaccina....
-
- National Centre for Immunisation Research and Surveillance , Significant Events in Influenza Vaccination Practice in Australia[Internet] (NSW: National Centre for Immunisation Research and Surveillance, 2022. [cited 2024 Jan 14]. Available from:), https://ncirs.org.au/sites/default/files/2022‐11/Influenza‐history‐Novem....
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

